Page 285 - Mechanical design of microresonators _ modeling and applications
P. 285
0-07-145538-8_CH05_284_08/30/05
Resonant Micromechanical Systems
284 Chapter Five
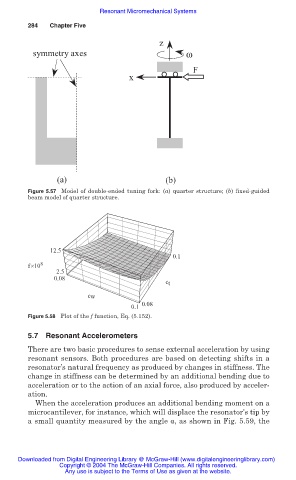
z
symmetry axes ω
F
x
(a) (b)
Figure 5.57 Model of double-ended tuning fork: (a) quarter structure; (b) fixed-guided
beam model of quarter structure.
12.5
0.1
f×10 8
2.5
0.08
c t
cw
0.1 0.08
Figure 5.58 Plot of the f function, Eq. (5.152).
5.7 Resonant Accelerometers
There are two basic procedures to sense external acceleration by using
resonant sensors. Both procedures are based on detecting shifts in a
resonator’s natural frequency as produced by changes in stiffness. The
change in stiffness can be determined by an additional bending due to
acceleration or to the action of an axial force, also produced by acceler-
ation.
When the acceleration produces an additional bending moment on a
microcantilever, for instance, which will displace the resonator’s tip by
a small quantity measured by the angle Į, as shown in Fig. 5.59, the
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.