Page 188 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 188
176 MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
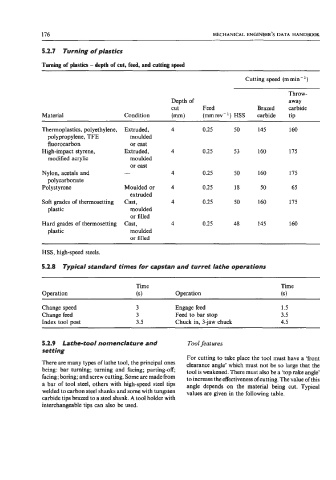
5.2.7 Turning of plastics
Turning of plastics - depth of cut, feed, and cutting sped
Cutting speed (m min- ’)
Throw-
Depth of away
cut Feed Brazed carbide
Material Condition (mm) (mm rev- ’) HSS carbide tip
Thermoplastics, polyethylene, Extruded, 4 0.25 50 145 160
polypropylene, TFE moulded
fluorocarbon or cast
High-impact styrene, Extruded, 4 0.25 53 160 175
modified acrylic moulded
or cast
Nylon, acetals and - 4 0.25 50 160 175
polycarbonate
Polystyrene Moulded or 4 0.25 18 50 65
extruded
Soft grades of thermosetting Cast, 4 0.25 50 160 175
plastic moulded
or filled
Hard grades of thermosetting Cast, 4 0.25 48 145 160
plastic moulded
or filled
HSS, high-speed steels.
5.2.8 Typical standard times for capstan and turret lathe operations
Time Time
Operation (s) Operation (SI
Change speed 3 Engage feed 1.5
Change feed 3 Feed to bar stop 3.5
Index tool post 3.5 Chuck in, 3-jaw chuck 4.5
5.2.9 Lathe-tool nomenclature and Tool features
setting
For cutting to take place the tool must have a ‘front
There are many types of lathe tool, the principal ones clearance angle’ which must not be so large that the
being: bar turning; turning and facing; parting-off tool is weakened. There must also be a ‘top rake angle’
facing; boring; and screw cutting. Some are made from to increase the effectiveness of cutting. The value of this
a bar of tool steel, others with high-speed steel tips angle depends on the material being cut. Typical
welded to carbon steel shanks and some with tungsten values are given in the following table.
carbide tips brazed to a steel shank. A tool holder with
interchangeable tips can also be used.