Page 397 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 397
386 Cooling Electronic Equipment
5
Nu 0.069(Gr) 1 / 3 Pr 0.407 , 3 10 Ra 7 10 9 (33a)
where Ra is the Rayleigh number,
Ra GrPr (33b)
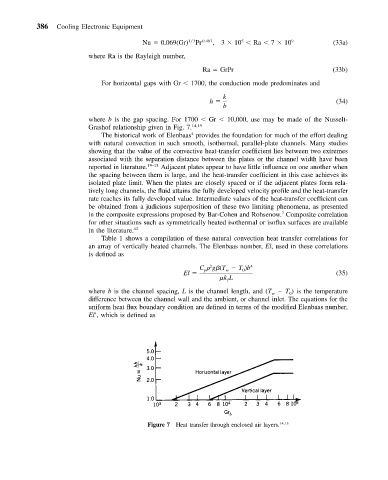
For horizontal gaps with Gr 1700, the conduction mode predominates and
k
h (34)
b
where b is the gap spacing. For 1700 Gr 10,000, use may be made of the Nusselt-
Grashof relationship given in Fig. 7. 14,15
4
The historical work of Elenbaas provides the foundation for much of the effort dealing
with natural convection in such smooth, isothermal, parallel-plate channels. Many studies
showing that the value of the convective heat-transfer coefficient lies between two extremes
associated with the separation distance between the plates or the channel width have been
reported in literature. 19–21 Adjacent plates appear to have little influence on one another when
the spacing between them is large, and the heat-transfer coefficient in this case achieves its
isolated plate limit. When the plates are closely spaced or if the adjacent plates form rela-
tively long channels, the fluid attains the fully developed velocity profile and the heat-transfer
rate reaches its fully developed value. Intermediate values of the heat-transfer coefficient can
be obtained from a judicious superposition of these two limiting phenomena, as presented
7
in the composite expressions proposed by Bar-Cohen and Rohsenow. Composite correlation
for other situations such as symmetrically heated isothermal or isoflux surfaces are available
in the literature. 42
Table 1 shows a compilation of these natural convection heat transfer correlations for
an array of vertically heated channels. The Elenbaas number, El, used in these correlations
is defined as
2
C g (T T )b 4
El p w 0 (35)
kL
ƒ
where b is the channel spacing, L is the channel length, and (T T ) is the temperature
0
w
difference between the channel wall and the ambient, or channel inlet. The equations for the
uniform heat flux boundary condition are defined in terms of the modified Elenbaas number,
El
, which is defined as
Figure 7 Heat transfer through enclosed air layers. 14,15