Page 268 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 268
Carbenes 257
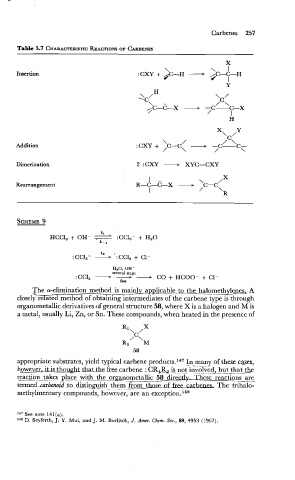
Table 5.7 CHARACTERISTIC ACTIONS OF CARBENES
\ \ I
'
Insertion : CXY + $C-H - /C-C-H I
Y
Addition
Dimerization 2 : CXY - XYC=CXY
Rearrangement
k
HCCI, + OH- + CC1,- + H20
:
k-1
H,O, OH -
several steps
CO
:CC& * - * + HCOO- + C1-
fast
he a-elimination method is mainly applicable to the halomethylds> A
close1:related method of obtaining intermediates of the carbene type is through
organometallic derivatives of general structure 58, where X is a halogen and M is
a metal, usually Li, Zn, or Sn. These compounds, when heated in the presence of
appropriate substrates, yield typical carbene pr0d~cts.l~~ In many of these cases,
however, it is thou~h~dmtthe free carbene : CR,R,is no_t_iGl;ed, but that tke
reaction takes place gth the organometallic 58 dire- These reactions a2
tdcaxhenoid to distinggish them _. from thosf:f free carbenes. The trihalo-
_
methylmercury compounds, however, are an exception.14'
14' See note 141 (a).
140 D. Seyferth, J. Y. Mui, and J. M. Burlitch, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 89, 4953 (1967).