Page 163 - Mechatronic Systems Modelling and Simulation with HDLs
P. 163
152 7 MECHATRONICS
4.0
Type 1
Type 2 CR123A
Type 3
(A) 2.0
T = − 20 C
T = 20 C
0.0
4.0
AlMn
(A) 2.0
T = − 20 C
T = 20 C
0.0
4.0
NiCd
(A) 2.0
T = − 20 C
T = 20 C
0.0
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
t(s)
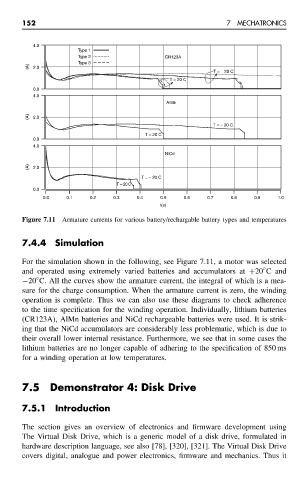
Figure 7.11 Armature currents for various battery/rechargable battery types and temperatures
7.4.4 Simulation
For the simulation shown in the following, see Figure 7.11, a motor was selected
◦
and operated using extremely varied batteries and accumulators at +20 C and
◦
−20 C. All the curves show the armature current, the integral of which is a mea-
sure for the charge consumption. When the armature current is zero, the winding
operation is complete. Thus we can also use these diagrams to check adherence
to the time specification for the winding operation. Individually, lithium batteries
(CR123A), AlMn batteries and NiCd rechargeable batteries were used. It is strik-
ing that the NiCd accumulators are considerably less problematic, which is due to
their overall lower internal resistance. Furthermore, we see that in some cases the
lithium batteries are no longer capable of adhering to the specification of 850 ms
for a winding operation at low temperatures.
7.5 Demonstrator 4: Disk Drive
7.5.1 Introduction
The section gives an overview of electronics and firmware development using
The Virtual Disk Drive, which is a generic model of a disk drive, formulated in
hardware description language, see also [78], [320], [321]. The Virtual Disk Drive
covers digital, analogue and power electronics, firmware and mechanics. Thus it