Page 235 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 235
Circuit Design 207
1.0
V g V gs = 1.5 V
V = V g − V s
gs
0.8 V s V d
V ds = V d − V s V = 1.3 V
Relative current (A) 0.6 V = 1.1 V
gs
0.4
gs
0.2 Linear Saturation V = 0.9 V
gs
V = 0.0 V
gs
0.0
0 0.3 0.6 0.9 1.2 1.5
V (V)
ds
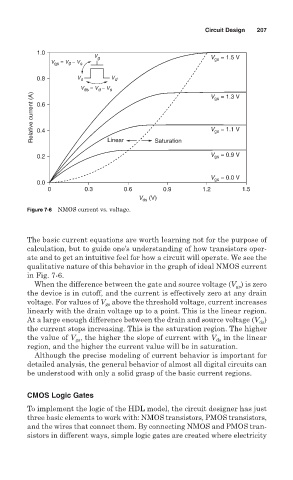
Figure 7-6 NMOS current vs. voltage.
The basic current equations are worth learning not for the purpose of
calculation, but to guide one’s understanding of how transistors oper-
ate and to get an intuitive feel for how a circuit will operate. We see the
qualitative nature of this behavior in the graph of ideal NMOS current
in Fig. 7-6.
When the difference between the gate and source voltage (V ) is zero
gs
the device is in cutoff, and the current is effectively zero at any drain
voltage. For values of V above the threshold voltage, current increases
gs
linearly with the drain voltage up to a point. This is the linear region.
At a large enough difference between the drain and source voltage (V )
ds
the current stops increasing. This is the saturation region. The higher
the value of V , the higher the slope of current with V ds in the linear
gs
region, and the higher the current value will be in saturation.
Although the precise modeling of current behavior is important for
detailed analysis, the general behavior of almost all digital circuits can
be understood with only a solid grasp of the basic current regions.
CMOS Logic Gates
To implement the logic of the HDL model, the circuit designer has just
three basic elements to work with: NMOS transistors, PMOS transistors,
and the wires that connect them. By connecting NMOS and PMOS tran-
sistors in different ways, simple logic gates are created where electricity