Page 48 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 48
24 Chapter One
Solution Problem
Channel length reduction Increased subthreshold leakage
Oxide thickness reduction Oxide breakdown and gate leakage
Supply voltage reduction Reduced performance
Threshold voltage reduction Increased subthreshold leakage
New transistor structure??
Figure 1-11 MOSFET scaling flow.
Interconnect scaling
Fitting more transistors onto a die requires not only shrinking the tran-
sistors but also shrinking the wires that interconnect them. To connect
millions of transistors modern microprocessors may use seven or more
separate layers of wires. These interconnects contribute to the delay of
the overall circuit. They add capacitive load to the transistor outputs,
and their resistance means that voltages take time to travel their length.
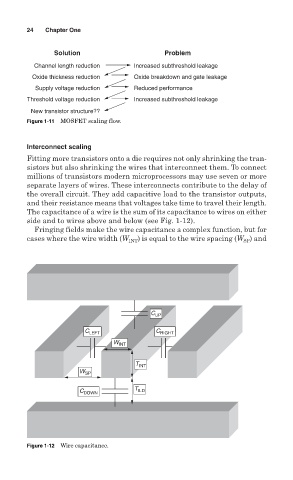
The capacitance of a wire is the sum of its capacitance to wires on either
side and to wires above and below (see Fig. 1-12).
Fringing fields make the wire capacitance a complex function, but for
cases where the wire width (W INT ) is equal to the wire spacing (W ) and
SP
C UP
C LEFT C RIGHT
W INT
T INT
W SP
C DOWN T ILD
Figure 1-12 Wire capacitance.