Page 43 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 43
ETCHING ELECTRONIC MATERIALS 25
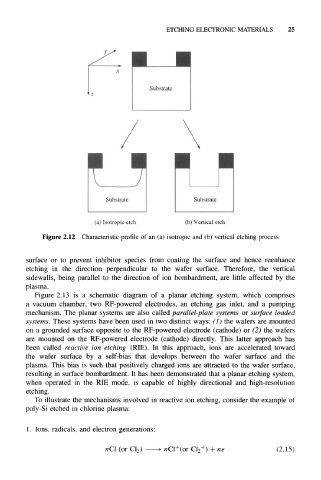
(a) Isotropic etch (b) Vertical etch
Figure 2.12 Characteristic profile of an (a) isotropic and (b) vertical etching process
surface or to prevent inhibitor species from coating the surface and hence reenhance
etching in the direction perpendicular to the wafer surface. Therefore, the vertical
sidewalls, being parallel to the direction of ion bombardment, are little affected by the
plasma.
Figure 2.13 is a schematic diagram of a planar etching system, which comprises
a vacuum chamber, two RF-powered electrodes, an etching gas inlet, and a pumping
mechanism. The planar systems are also called parallel-plate systems or surface loaded
systems. These systems have been used in two distinct ways: (1) the wafers are mounted
on a grounded surface opposite to the RF-powered electrode (cathode) or (2) the wafers
are mounted on the RF-powered electrode (cathode) directly. This latter approach has
been called reactive ion etching (RIE). In this approach, ions are accelerated toward
the wafer surface by a self-bias that develops between the wafer surface and the
plasma. This bias is such that positively charged ions are attracted to the wafer surface,
resulting in surface bombardment. It has been demonstrated that a planar etching system,
when operated in the RIE mode, is capable of highly directional and high-resolution
etching.
To illustrate the mechanisms involved in reactive ion etching, consider the example of
poly-Si etched in chlorine plasma:
1. Ions, radicals, and electron generations:
+
+
(or C1 2) > nCl (or C1 2 ) + ne (2.15)