Page 74 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 74
SEMICONDUCTORS 55
in a furnace with different carbon-releasing materials such as coal and coke. Several
reactions take place inside the furnace and the net reaction that results in silicon is
SiC + SiO 2 Si + SiO (gas) + CO (gas) (3.3)
The silicon so produced is called metallurgical-grade silicon (MGS), which contains up
to 2 percent impurities. Subsequently, the silicon is treated with hydrogen chloride (HC1)
to form trichlorosilane (SiHCl 3):
Si + 3HC1 SiHCl 3 (gas) + H 2 (gas) (3.4)
is liquid at room temperature. Fractional distillation of the SiHCl 3 liquid removes
impurities, and the purified liquid is reduced in a hydrogen atmosphere to yield electronic-
grade silicon (EGS) through the reaction
SiHCl 3 + H Si + 3HC1 (3.5)
EGS is a polycrystalline material of remarkably high purity and is used as the raw material
for preparing high-quality silicon wafers.
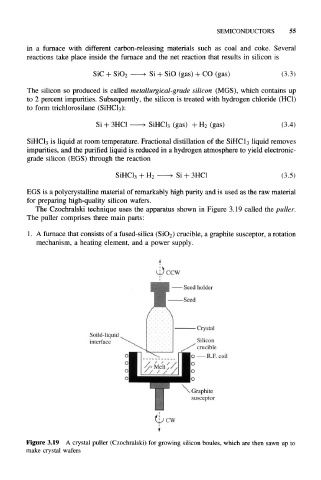
The Czochralski technique uses the apparatus shown in Figure 3.19 called the puller.
The puller comprises three main parts:
1. A furnace that consists of a fused-silica (SiO 2) crucible, a graphite susceptor, a rotation
mechanism, a heating element, and a power supply.
CCW
Seed holder
Seed
Soild-liquid
interface
Graphite
susceptor
Figure 3.19 A crystal puller (Czochralski) for growing silicon boules, which are then sawn up to
make crystal wafers