Page 168 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 168
138 Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
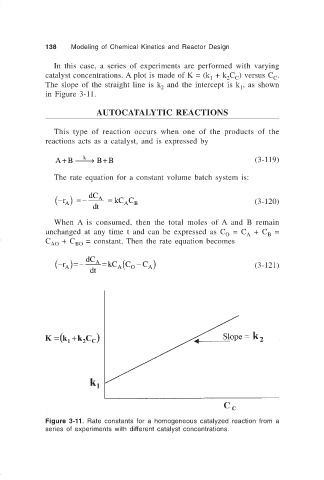
In this case, a series of experiments are performed with varying
catalyst concentrations. A plot is made of K = (k + k C ) versus C .
1
C
2 C
The slope of the straight line is k and the intercept is k , as shown
2
1
in Figure 3-11.
AUTOCATALYTIC REACTIONS
This type of reaction occurs when one of the products of the
reactions acts as a catalyst, and is expressed by
+
+
AB → B B (3-119)
k
The rate equation for a constant volume batch system is:
− ( r A ) =− dC A = kC C B (3-120)
A
dt
When A is consumed, then the total moles of A and B remain
unchanged at any time t and can be expressed as C = C + C =
O
A
B
C AO + C BO = constant. Then the rate equation becomes
− ( r A )=− dC A = kC A (C O − C A ) (3-121)
dt
Figure 3-11. Rate constants for a homogeneous catalyzed reaction from a
series of experiments with different catalyst concentrations.