Page 185 - Modern Control Systems
P. 185
Terms and Concepts 159
T d(s) — lis) and co-plot the steady-state value of (c) Determine the value of K such that the steady-
the output Y (s) as a function of the controller gain state value of the output is equal for both the
0 < K < 10 on the same plot as in (a) above. input response and the disturbance response.
' ' »
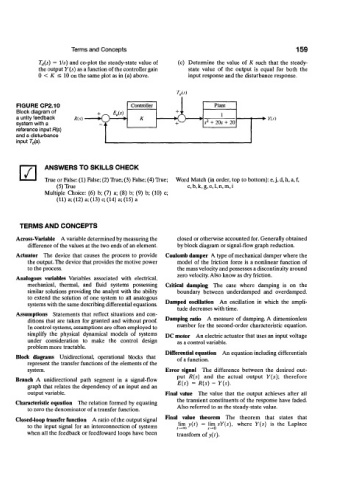
FIGURE CP2.10
Block diagram of
a unity feedback R(s) *> Y(s)
system with a
reference input R[s)
and a disturbance
input T d(s).
ANSWERS TO SKILLS CHECK
m True or False: (1) False; (2) True; (3) False; (4) True; Word Match (in order, top to bottom): e, , j d, h, a, f,
(5) True c, b, k, g, o, 1, n, m, i
Multiple Choice: (6) b; (7) a; (8) b; (9) b; (10) c;
(11) a; (12) a; (13) c; (14) a; (15) a
TERMS AND CONCEPTS
Across-Variable A variable determined by measuring the closed or otherwise accounted for. Generally obtained
difference of the values at the two ends of an element. by block diagram or signal-flow graph reduction.
Actuator The device that causes the process to provide Coulomb damper A type of mechanical damper where the
the output. The device that provides the motive power model of the friction force is a nonlinear function of
to the process. the mass velocity and possesses a discontinuity around
zero velocity. Also know as dry friction.
Analogous variables Variables associated with electrical,
mechanical, thermal, and fluid systems possessing Critical damping The case where damping is on the
similar solutions providing the analyst with the ability boundary between underdamped and overdamped.
to extend the solution of one system to all analogous
systems with the same describing differential equations. Damped oscillation An oscillation in which the ampli-
tude decreases with time.
Assumptions Statements that reflect situations and con-
ditions that are taken for granted and without proof. Damping ratio A measure of damping. A dimensionless
In control systems, assumptions are often employed to number for the second-order characteristic equation.
simplify the physical dynamical models of systems DC motor An electric actuator that uses an input voltage
under consideration to make the control design as a control variable.
problem more tractable.
Differential equation An equation including differentials
Block diagrams Unidirectional, operational blocks that of a function.
represent the transfer functions of the elements of the
system. Error signal The difference between the desired out-
put R{s) and the actual output Y(s); therefore
Branch A unidirectional path segment in a signal-flow E{s) = R(s) - Y(s).
graph that relates the dependency of an input and an
output variable. Final value The value that the output achieves after all
Characteristic equation The relation formed by equating the transient constituents of the response have faded.
to zero the denominator of a transfer function. Also referred to as the steady-state value.
Closed-loop transfer function A ratio of the output signal Final value theorem The theorem that states that
to the input signal for an interconnection of systems lim y(t) = lim .sY(.y), where Y(s) is the Laplace
when all the feedback or feedfoward loops have been transform of y(t).