Page 177 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 177
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 79
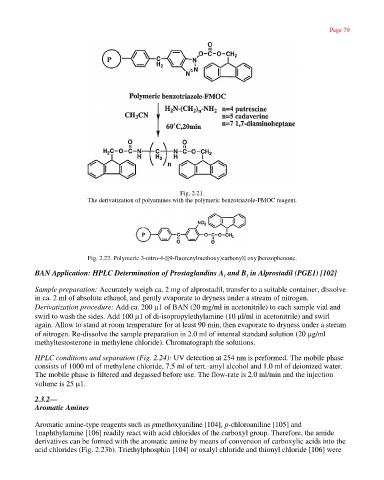
Fig. 2.21.
The derivatization of polyamines with the polymeric benzotriazole-FMOC reagent.
Fig. 2.22. Polymeric 3-nitro-4-[[9-fluorenylmethoxy)carbonyl] oxy]benzophenone.
BAN Application: HPLC Determination of Prostaglandins A and B in Alprostadil (PGE1) [102]
1 1
Sample preparation: Accurately weigh ca. 2 mg of alprostadil, transfer to a suitable container, dissolve
in ca. 2 ml of absolute ethanol, and gently evaporate to dryness under a stream of nitrogen.
Derivatization procedure: Add ca. 200 µ1 of BAN (20 mg/ml in acetonitrile) to each sample vial and
swirl to wash the sides. Add 100 µ1 of di-isopropylethylamine (10 µl/ml in acetonitrile) and swirl
again. Allow to stand at room temperature for at least 90 min, then evaporate to dryness under a stream
of nitrogen. Re-dissolve the sample preparation in 2.0 ml of internal standard solution (20 µg/ml
methyltestosterone in methylene chloride). Chromatograph the solutions.
HPLC conditions and separation (Fig. 2.24): UV detection at 254 nm is performed. The mobile phase
consists of 1000 ml of methylene chloride, 7.5 ml of tert.-amyl alcohol and 1.0 ml of deionized water.
The mobile phase is filtered and degassed before use. The flow-rate is 2.0 ml/min and the injection
volume is 25 µ1.
2.3.2—
Aromatic Amines
Aromatic amine-type reagents such as pmethoxyaniline [104], p-chloroaniline [105] and
1naphthylamine [106] readily react with acid chlorides of the carboxyl group. Therefore, the amide
derivatives can be formed with the aromatic amine by means of conversion of carboxylic acids into the
acid chlorides (Fig. 2.23b). Triethylphosphin [104] or oxalyl chloride and thionyl chloride [106] were
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_79.html 30/09/2003