Page 221 - Modern physical chemistry
P. 221
214 Electrochemistry
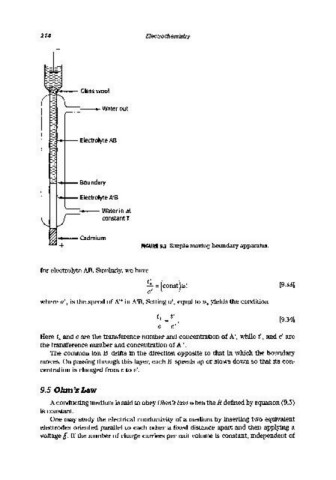
~,..-- Glass wool
_Waterout
~+-- Electrolyte AS
~I-.j-- Boundary
I~!--- Electrolyte A'B
-Waterinat
constant T
FIGURE 9.2 Simple moving boundary apparatus.
for electrolyte AB. Similarly, we have
:~ = (const )u~ [9.33]
where u'+ is the speed of AI+ in A'B. Setting u'+ equal to u. yields the condition
[9.34]
c c'
Here t+ and c are the transference number and concentration of A+, while t'+ and c' are
the transference number and concentration of A'·.
The cornmon ion B- drifts in the direction opposite to that in which the boundary
moves. On passing through this layer, each B- speeds up or slows down so that its con-
centration is changed from c to c'.
9.S Ohm's Law
A conducting medium is said to obey Ohm s law when the R defined by equation (9.5)
is constant.
One may study the electrical conductivity of a medium by inserting two equivalent
electrodes oriented parallel to each other a fixed distance apart and then applying a
voltage t. If the number of charge carriers per unit volume is constant, independent of