Page 243 - Modular design for machine tools
P. 243
Basic Knowledge of Machine Tool Joints 203
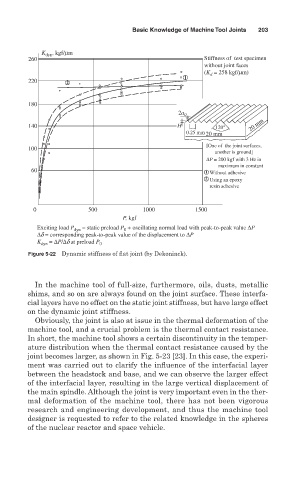
K dyn , kgf/mm
260 Stiffness of test specimen
without joint faces
(K = 258 kgf/mm)
d
1
220 2
180
2a 0
140 H 120° 20 mm
0.25 mm 20 mm
[One of the joint surfaces,
100
another is ground]
∆P = 200 kgf with 3 Hz in
maximum in constant
60 1 Without adhesive
2 Using an epoxy
resin adhesive
0 500 1000 1500
P, kgf
Exciting load P dyn = static preload P + oscillating normal load with peak-to-peak value ∆P
0
∆d = corresponding peak-to-peak value of the displacement to ∆P
K dyn = ∆P/∆d at preload P 0
Figure 5-22 Dynamic stiffness of flat joint (by Dekoninck).
In the machine tool of full-size, furthermore, oils, dusts, metallic
shims, and so on are always found on the joint surface. These interfa-
cial layers have no effect on the static joint stiffness, but have large effect
on the dynamic joint stiffness.
Obviously, the joint is also at issue in the thermal deformation of the
machine tool, and a crucial problem is the thermal contact resistance.
In short, the machine tool shows a certain discontinuity in the temper-
ature distribution when the thermal contact resistance caused by the
joint becomes larger, as shown in Fig. 5-23 [23]. In this case, the experi -
ment was carried out to clarify the influence of the interfacial layer
between the headstock and base, and we can observe the larger effect
of the interfacial layer, resulting in the large vertical displacement of
the main spindle. Although the joint is very important even in the ther-
mal deformation of the machine tool, there has not been vigorous
research and engineering development, and thus the machine tool
designer is requested to refer to the related knowledge in the spheres
of the nuclear reactor and space vehicle.