Page 242 - Modular design for machine tools
P. 242
202 Engineering Design for Machine Tool Joints
1.4 b* values
1.2 ground 7.5
Flatness deviation for ground
1.0
0.8 5.0
b*, mm –1
0.6 Flatness deviation, mm
0.4 2.5
b* values
0.2 shaped
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Diameter of joint, mm
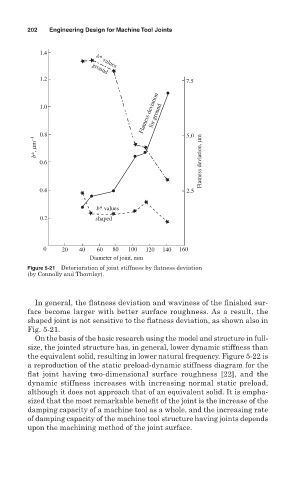
Figure 5-21 Deterioration of joint stiffness by flatness deviation
(by Connolly and Thornley).
In general, the flatness deviation and waviness of the finished sur-
face become larger with better surface roughness. As a result, the
shaped joint is not sensitive to the flatness deviation, as shown also in
Fig. 5-21.
On the basis of the basic research using the model and structure in full-
size, the jointed structure has, in general, lower dynamic stiffness than
the equivalent solid, resulting in lower natural frequency. Figure 5-22 is
a reproduction of the static preload-dynamic stiffness diagram for the
flat joint having two-dimensional surface roughness [22], and the
dynamic stiffness increases with increasing normal static preload,
although it does not approach that of an equivalent solid. It is empha-
sized that the most remarkable benefit of the joint is the increase of the
damping capacity of a machine tool as a whole, and the increasing rate
of damping capacity of the machine tool structure having joints depends
upon the machining method of the joint surface.