Page 182 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 182
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 3 CHARACTERISTICS AND BEHAVIOR OF NANOPARTICLES AND ITS DISPERSION SYSTEMS
used to characterize the dispersion behavior of parti- (3) Control of aggregation and dispersion
cles larger than submicronmeter in diameter. Few For the control of dispersion and aggregation of
papers have been published for nanoparticles using nanoparticles in gas phase, various methods have been
this method. investigated. One method is mechanical or hydrody-
For the characterization of dispersion behavior of namic dispersion of aggregate structure. This method
nanoparticles in gas phase, aggregate size distribution is applied for particles with larger than submicron-
was measured by nanoparticle measurement method in meter in diameter in the field of aerosol science and
gas phase such as low-pressure cascade impactor or technology. This method is classified into some types
differential mobility analyzer DMA. The ratio of mean according to the application method of mechanical
aggregate size to the mean primary particle size deter- and/or hydrodynamic interaction between particles,
mined from the distribution by the image processing of for example, acceleration by airflow, collision to the
TEM observation as shown in Fig. 3.6.3 was calculated obstructed plate, and mechanical dispersion by the
and defined as aggregation index. The overlapped area moving medium. The representative dispersing princi-
of both distributions in this figure was defined as the ples by each method are shown in Fig. 3.6.4. Airflow
amount of primary particles without aggregation. The acceleration method gives a fluid drag to particles by
ratio of this amount to the total particles was defined as using ejector or orifice with rapid reduction in the
dispersibility [6]. If all particles are dispersed to the cross section. Collision method disperses and col-
primary particles, since both size distributions per- lapses aggregate structure by the collision of aerosol to
fectly agree, the dispersibility is 1. If the aggregation of the plate. Fluidized bed or vibration is a popular
particles in aerosol is promoted, the overlapped area method that uses fluidized medium. By the movement
and the value of dispersibility are reduced. of medium, the aggregate structure is dispersed.
However, it is difficult to disperse the aggregates of
nanoparticles completely down to primary particles by
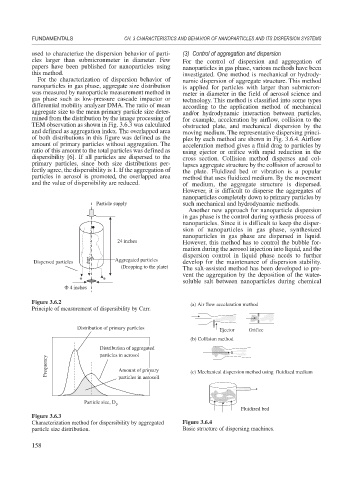
Particle supply such mechanical and hydrodynamic methods.
Another new approach for nanoparticle dispersion
in gas phase is the control during synthesis process of
nanoparticles. Since it is difficult to keep the disper-
sion of nanoparticles in gas phase, synthesized
nanoparticles in gas phase are dispersed in liquid.
24 inches However, this method has to control the bubble for-
mation during the aerosol injection into liquid, and the
dispersion control in liquid phase needs to further
Aggregated particles
Dispersed particles develop for the maintenance of dispersion stability.
(Dropping to the plate) The salt-assisted method has been developed to pre-
vent the aggregation by the deposition of the water-
soluble salt between nanoparticles during chemical
Φ 4 inches
Figure 3.6.2
(a) Air flow acceleration method
Principle of measurement of dispersibility by Carr.
Distribution of primary particles Ejector Orifice
(b) Collision method
Distribution of aggregated
particles in aerosol
Frequency Amount of primary
particles in aerosoll (c) Mechanical dispersion method using fluidized medium
Particle size, D p
Fluidized bed
Figure 3.6.3
Characterization method for dispersibility by aggregated Figure 3.6.4
particle size distribution. Basic structure of dispersing machines.
158