Page 215 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 215
4.3 NANOPORE STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS
O
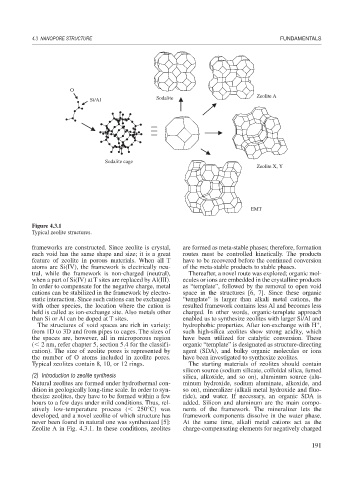
Si/Al Sodalite Zeolite A
Sodalite cage
Zeolite X, Y
EMT
Figure 4.3.1
Typical zeolite structures.
frameworks are constructed. Since zeolite is crystal, are formed as meta-stable phases; therefore, formation
each void has the same shape and size; it is a great routes must be controlled kinetically. The products
feature of zeolite in porous materials. When all T have to be recovered before the continued conversion
atoms are Si(IV), the framework is electrically neu- of the meta-stable products to stable phases.
tral, while the framework is non-charged (neutral), Thereafter, a novel route was explored; organic mol-
when a part of Si(IV) at T sites are replaced by Al(III). ecules or ions are embedded in the crystalline products
In order to compensate for the negative charge, metal as “template”, followed by the removal to open void
cations can be stabilized in the framework by electro- space in the structures [6, 7]. Since these organic
static interaction. Since such cations can be exchanged “template” is larger than alkali metal cations, the
with other species, the location where the cation is resulted framework contains less Al and becomes less
held is called as ion-exchange site. Also metals other charged. In other words, organic-template approach
than Si or Al can be doped at T sites. enabled us to synthesize zeolites with larger Si/Al and
The structures of void spaces are rich in variety: hydrophobic properties. After ion-exchange with H ,
from 1D to 3D and from pipes to cages. The sizes of such high-silica zeolites show strong acidity, which
the spaces are, however, all in microporous region have been utilized for catalytic conversion. These
( 2 nm, refer chapter 5, section 5.4 for the classifi- organic “template” is designated as structure-directing
cation). The size of zeolite pores is represented by agent (SDA), and bulky organic molecules or ions
the number of O atoms included in zeolite pores. have been investigated to synthesize zeolites.
Typical zeolites contain 8, 10, or 12 rings. The starting materials of zeolites should contain
silicon source (sodium silicate, colloidal silica, fumed
(2) Introduction to zeolite synthesis silica, alkoxide, and so on), aluminum source (alu-
Natural zeolites are formed under hydrothermal con- minum hydroxide, sodium aluminate, alkoxide, and
dition in geologically long-time scale. In order to syn- so on), mineralizer (alkali metal hydroxide and fluo-
thesize zeolites, they have to be formed within a few ride), and water. If necessary, an organic SDA is
hours to a few days under mild conditions. Thus, rel- added. Silicon and aluminum are the main compo-
atively low-temperature process ( 250°C) was nents of the framework. The mineralizer lets the
developed, and a novel zeolite of which structure has framework components dissolve in the water phase.
never been found in natural one was synthesized [5]: At the same time, alkali metal cations act as the
Zeolite A in Fig. 4.3.1. In these conditions, zeolites charge-compensating elements for negatively charged
191