Page 217 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 217
4.3 NANOPORE STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS
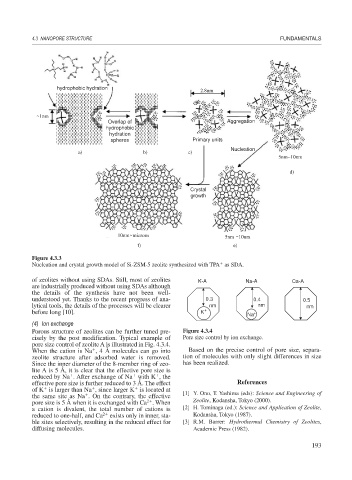
hydrophobic hydration
2.8nm
~1nm
Overlap of Aggregation
hydrophobic
hydration
spheres Primary units
Nucleation
a) b) c)
5nm~10nm
d)
Crystal
growth
10nm ~microns 5nm ~10nm
f) e)
Figure 4.3.3
Nucleation and crystal growth model of Si-ZSM-5 zeolite synthesized with TPA as SDA.
of zeolites without using SDAs. Still, most of zeolites K-A Na-A Ca-A
are industrially produced without using SDAs although
the details of the synthesis have not been well-
understood yet. Thanks to the recent progress of ana- 0.3 0.4 0.5
lytical tools, the details of the processes will be clearer nm nm nm
before long [10]. K + Na +
(4) Ion exchange
Porous structure of zeolites can be further tuned pre- Figure 4.3.4
cisely by the post modification. Typical example of Pore size control by ion exchange.
pore size control of zeolite A is illustrated in Fig. 4.3.4.
When the cation is Na , 4 Å molecules can go into Based on the precise control of pore size, separa-
zeolite structure after adsorbed water is removed. tion of molecules with only slight differences in size
Since the inner diameter of the 8-member ring of zeo- has been realized.
lite A is 5 Å, it is clear that the effective pore size is
reduced by Na . After exchange of Na with K , the
effective pore size is further reduced to 3 Å. The effect References
of K is larger than Na , since larger K is located at [1] Y. Ono, T. Yashima (eds): Science and Engineering of
the same site as Na . On the contrary, the effective
2
pore size is 5 Å when it is exchanged with Ca . When Zeolite, Kodansha, Tokyo (2000).
a cation is divalent, the total number of cations is [2] H. Tominaga (ed.): Science and Application of Zeolite,
reduced to one-half, and Ca 2 exists only in inner, sta- Kodansha, Tokyo (1987).
ble sites selectively, resulting in the reduced effect for [3] R.M. Barrer: Hydrothermal Chemistry of Zeolites,
diffusing molecules. Academic Press (1982).
193