Page 253 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 253
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 4 CONTROL OF NANOSTRUCTURE OF MATERIALS
generally ranges from submicron to a few microns and influence the sintering behavior and microstructure of
no report using nanoparticles has been issued to date. the material during the firing process.
There is a unique LTCC of CaO-Al O -SiO -B O -
3
2
2
2
3
system glass ceramics, which starts from the “Glass (3) Control of the microstructure
composite system” after the above classification of a The major important factors influencing the sintering
mixture of aggregates like Al O and glass as raw behavior and microstructure are the particles, forming
2
3
materials. However, this shows the properties of a and firing, respectively. The influencing factors of the
“Crystallized glass system” generating crystals from particles are particle size, size distribution, surface
the glass during the firing. condition, synthetic method, and agglomeration, etc.
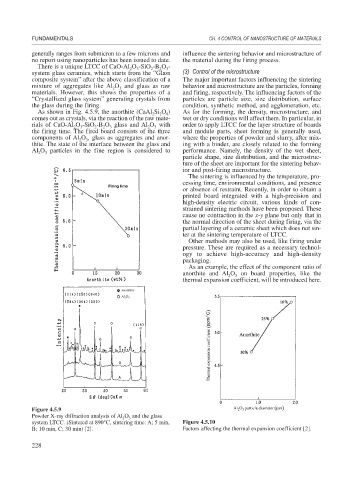
As shown in Fig. 4.5.9, the anorthite (CaAl Si O ) As for the forming, the density, microstructure, and
2
8
2
comes out as crystals, via the reaction of the raw mate- wet or dry conditions will affect them. In particular, in
rials of CaO-Al O -SiO -B O glass and Al O with order to apply LTCC for the layer structure of boards
2
2
3
2
3
2
3
the firing time. The fired board consists of the three and module parts, sheet forming is generally used,
components of Al O , glass as aggregates and anor- where the properties of powder and slurry, after mix-
3
2
thite. The state of the interface between the glass and ing with a binder, are closely related to the forming
Al O particles in the fine region is considered to performance. Namely, the density of the wet sheet,
3
2
particle shape, size distribution, and the microstruc-
ture of the sheet are important for the sintering behav-
ior and post-firing microstructure.
The sintering is influenced by the temperature, pro-
cessing time, environmental conditions, and presence
or absence of restraint. Recently, in order to obtain a
printed board integrated with a high-precision and
high-density electric circuit, various kinds of con-
strained sintering methods have been proposed. These
cause no contraction in the x-y plane but only that in
the normal direction of the sheet during firing, via the
partial layering of a ceramic sheet which does not sin-
ter at the sintering temperature of LTCC.
Other methods may also be used, like firing under
pressure. These are required as a necessary technol-
ogy to achieve high-accuracy and high-density
packaging.
As an example, the effect of the component ratio of
anorthite and Al O on board properties, like the
2
3
thermal expansion coefficient, will be introduced here.
Figure 4.5.9
Powder X-ray diffraction analysis of Al O and the glass
2
3
system LTCC. (Sintered at 890°C, sintering time: A; 5 min, Figure 4.5.10
B; 10 min, C; 30 min) [2]. Factors affecting the thermal expansion coefficient [2].
228