Page 377 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 377
6.4 ELECTRIC PROPERTIES FUNDAMENTALS
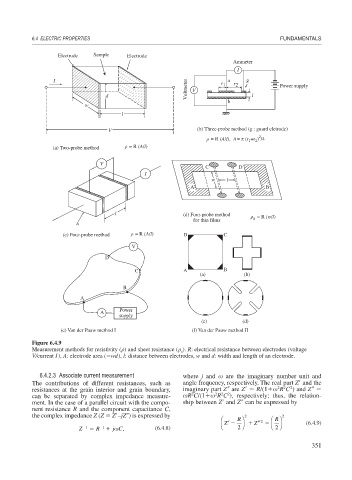
Electrode Sample Electrode
Ammeter
I
I r 1 a r 2 g
Voltmeter V Power supply
d l
b
w
l
V (b) Three-probe method (g : guard eletrode)
2
= R (A/l), A =
(r +r ) /4
2
1
(a) Two-probe method = R (A/l)
V
C D
I
w l
A B
l (d) Four-probe method = R (w/l)
for thin films s
A
(c) Four-probe method = R (A/l) D C
V
D
C A B
(a) (b)
B
A
Power
A
supply
(c) (d)
(e) Van der Pauw method I (f) Van der Pauw method II
Figure 6.4.9
Measurement methods for resistivity ( ) and sheet resistance ( ). R: electrical resistance between electrodes (voltage
s
V/current I), A: electrode area ( wd), l: distance between electrodes, w and d: width and length of an electrode.
6.4.2.3 Associate current measurement where j and are the imaginary number unit and
The contributions of different resistances, such as angle frequency, respectively. The real part Z and the
2
2 2
resistances at the grain interior and grain boundary, imaginary part Z are Z R/(1 R C ) and Z
2
2 2
2
can be separated by complex impedance measure- R C/(1 R C ), respectively; thus, the relation-
ment. In the case of a parallel circuit with the compo- ship between Z and Z can be expressed by
nent resistance R and the component capacitance C,
the complex impedance Z (Z Z –jZ ) is expressed by 2 2
⎛ R ⎞ ⎛ ⎞
R
2
⎜ ′ Z ⎟ Z ′′ ⎜ ⎟ (6.4.9)
2
Z 1 R 1 j C, (6.4.8) ⎝ 2 ⎠ ⎝ ⎠
351