Page 39 - Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB and Excel
P. 39
Chapter 1 Introduction to MATLAB
600
400
Imaginary part of Z 200 0
-200
-400
-600
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000
radian frequency w
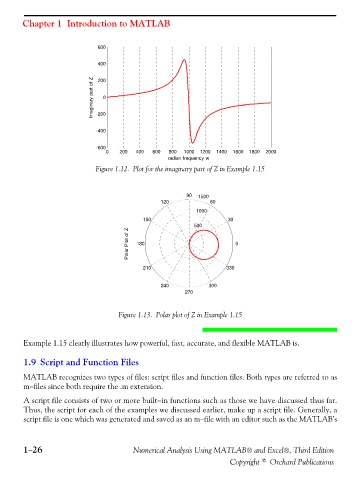
Figure 1.12. Plot for the imaginary part of Z in Example 1.15
90
1500
120 60
1000
150 30
500
Polar Plot of Z 180 0
210 330
240 300
270
Figure 1.13. Polar plot of Z in Example 1.15
Example 1.15 clearly illustrates how powerful, fast, accurate, and flexible MATLAB is.
1.9 Script and Function Files
MATLAB recognizes two types of files: script files and function files. Both types are referred to as
m−files since both require the .m extension.
A script file consists of two or more built−in functions such as those we have discussed thus far.
Thus, the script for each of the examples we discussed earlier, make up a script file. Generally, a
script file is one which was generated and saved as an m−file with an editor such as the MATLAB’s
1−26 Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB® and Excel®, Third Edition
Copyright © Orchard Publications