Page 279 - Op Amps Design, Applications, and Troubleshooting
P. 279
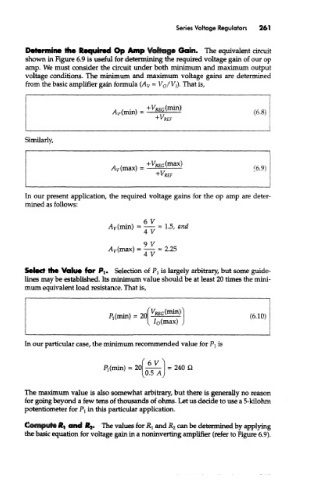
Series Voltage Regulators 261
Determine the Required Op Amp Voltage Gain. The equivalent circuit
shown in Figure 6.9 is useful for detennining the required voltage gain of our op
amp. We must consider the circuit under both minimum and maximum output
voltage conditions. The minimum and maximum voltage gains are determined
from the basic amplifier gain formula (A v = V o/V t). That is,
Similarly,
In our present application, the required voltage gains for the op amp are deter-
mined as follows:
6 V
Ay(min) = —- = 1.5, and
4 V
9
A v(max) = — = 2.25
Select the Value for P|» Selection of Pj is largely arbitrary, but some guide-
lines may be established. Its minimum value should be at least 20 times the mini-
mum equivalent load resistance. That is,
In our particular case, the minimum recommended value for PI is
The maximum value is also somewhat arbitrary, but there is generally no reason
for going beyond a few tens of thousands of ohms. Let us decide to use a 5-kilohm
potentiometer for P 1 in this particular application.
Compute Jtj and f^. The values for RI and R 2 can be determined by applying
the basic equation for voltage gain in a noninverting amplifier (refer to Figure 6.9).