Page 329 - Op Amps Design, Applications, and Troubleshooting
P. 329
ideal Clamper 307
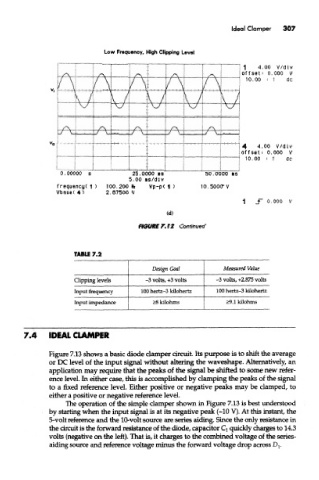
Low Frequency, High Clipping Level
TABLE 7.2
Design Goal Measured Value
Clipping levels -3 volts, +3 volts -3 volts, +2.875 volts
Input frequency 100 hertz-3 kilohertz 100 hertz-3 kilohertz
Input impedance >8 kilohms >9.1 kilohms
7.4 (DIAL CLAMPER
Figure 7.13 shows a basic diode clamper circuit. Its purpose is to shift the average
or DC level of the input signal without altering the waveshape. Alternatively, an
application may require that the peaks of the signal be shifted to some new refer-
ence level. In either case, this is accomplished by clamping the peaks of the signal
to a fixed reference level. Either positive or negative peaks may be clamped, to
either a positive or negative reference level.
The operation of the simple clamper shown in Figure 7.13 is best understood
by starting when the input signal is at its negative peak (-10 V). At this instant, the
5-volt reference and the 10-volt source are series aiding. Since the only resistance in
the circuit is the forward resistance of the diode, capacitor Q quickly charges to 14.3
volts (negative on the left). That is, it charges to the combined voltage of the series-
aiding source and reference voltage minus the forward voltage drop across D t.