Page 175 - Optofluidics Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications
P. 175
150 Cha pte r Se v e n
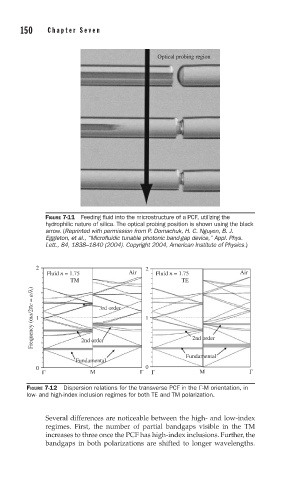
Optical probing region
FIGURE 7-11 Feeding fl uid into the microstructure of a PCF, utilizing the
hydrophilic nature of silica. The optical probing position is shown using the black
arrow. (Reprinted with permission from P. Domachuk, H. C. Nguyen, B. J.
Eggleton, et al., “Microfl uidic tunable photonic band-gap device,” Appl. Phys.
Lett., 84, 1838–1840 (2004). Copyright 2004, American Institute of Physics.)
2 2
Fluid n = 1.75 Air Fluid n = 1.75 Air
TM TE
Frequency (ωa/2πc = a/λ) 1 3rd order 1
2nd order
2nd order
Fundamental
Fundamental
0 0
Γ M Γ Γ M Γ
FIGURE 7-12 Dispersion relations for the transverse PCF in the Γ-M orientation, in
low- and high-index inclusion regimes for both TE and TM polarization.
Several differences are noticeable between the high- and low-index
regimes. First, the number of partial bandgaps visible in the TM
increases to three once the PCF has high-index inclusions. Further, the
bandgaps in both polarizations are shifted to longer wavelengths.