Page 444 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 444
–25.0 5 μm (1)
2 μm (2)
4
–20.0 1 μm (3) 3
500 nm (4)
270 nm (5) 2
–15.0
I ds (μA) 5
–10.0
1
–5.0
0.0
290 K 0 –10 –20 –30 –40
V g = –40 V
V ds (V)
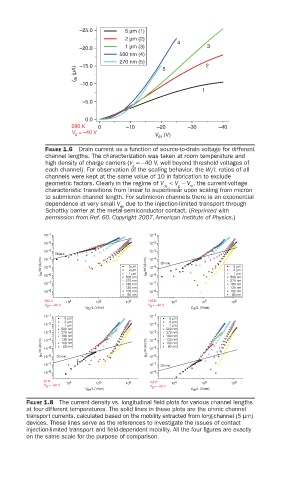
FIGURE 1.6 Drain current as a function of source-to-drain voltage for different
channel lengths. The characterization was taken at room temperature and
high density of charge carriers (V =−40 V, well beyond threshold voltages of
g
each channel). For observation of the scaling behavior, the W/L ratios of all
channels were kept at the same value of 10 in fabrication to exclude
geometric factors. Clearly in the regime of V < V − V , the current-voltage
ds g th
characteristic transitions from linear to superlinear upon scaling from micron
to submicron channel length. For submicron channels there is an exponential
dependence at very small V due to the injection-limited transport through
ds
Schottky barrier at the metal-semiconductor contact. (Reprinted with
permission from Ref. 60. Copyright 2007, American Institute of Physics.)
10 –1 10 –1
10 –2 10 –2
10 –3 10 –3
Ohmic 10 –4
10 –4
I ds /W (A/cm) 10 –5 5 μm I ds /W (A/cm) 10 –5 Ohmic 5 μm
2 μm
2 μm
1 μm
1 μm
10 –6
500 nm 10 –6 500 nm
270 nm 270 nm
10 –7 180 nm 10 –7 180 nm
130 nm 130 nm
10 –8 100 nm 10 –8 100 nm
80 nm 80 nm
290 K 10 4 10 5 10 6 125 K 10 4 10 5 10 6
V g = –40 V V g = –40 V
V ds /L (V/cm) V ds /L (V/cm)
10 –1 10 –1
5 μm 5 μm
2 μm 2 μm
10 –2 1 μm 10 –2 1 μm
500 nm 500 nm
10 –3 270 nm 10 –3 270 nm
180 nm 10 –4 180 nm
130 nm
130 nm
I ds /W (A/cm) 10 –5 100 nm I ds /W (A/cm) 10 –5 100 nm
10 –4
80 nm
80 nm
10 –6
10 –6
10 –7 Ohmic 10 –7 Ohmic
10 –8 10 –8
57 K 10 4 10 5 10 6 4.8 K 10 4 10 5 10 6
V g = –40 V V g = –40 V
V ds /L (V/cm) V ds /L (V/cm)
FIGURE 1.8 The current density vs. longitudinal fi eld plots for various channel lengths
at four different temperatures. The solid lines in these plots are the ohmic channel
transport currents, calculated based on the mobility extracted from long-channel (5 μm)
devices. These lines serve as the references to investigate the issues of contact
injection-limited transport and fi eld-dependent mobility. All the four fi gures are exactly
on the same scale for the purpose of comparison.