Page 284 - Origin and Prediction of Abnormal Formation Pressures
P. 284
256 H.H. RIEKE, G.V. CHILINGAR AND J.O. ROBERTSON JR.
g/kg
mg/kg
CI ~ = ~ ~
mg/kg
+~0. c,/B,~ ........
300 50 - 50-
200 25' 25'
SO~-~ -- ~~-
"I" Ma 2L - ,. ~ HCOa
100 a 0 0
CI/Br B Br 0 500 "1000 1500
Compaction pressure, kg/cm 2
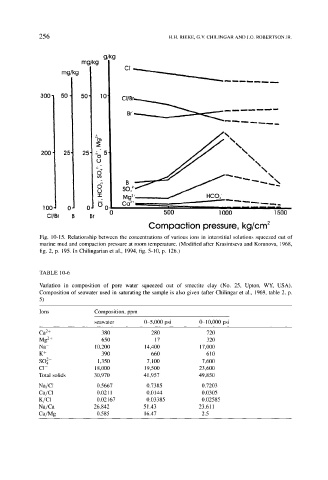
Fig. 10-15. Relationship between the concentrations of various ions in interstitial solutions squeezed out of
marine mud and compaction pressure at room temperature. (Modified after Krasintseva and Korunova, 1968,
fig. 2, p. 195. In Chilingarian et al., 1994, fig. 5-10, p. 126.)
TABLE 10-6
Variation in composition of pore water squeezed out of smectite clay (No. 25, Upton, WY, USA).
Composition of seawater used in saturating the sample is also given (after Chilingar et al., 1969, table 2, p.
5)
Ions Composition, ppm
seawater 0-5,000 psi 0-10,000 psi
Ca 2+ 380 280 720
Mg 2+ 650 17 320
Na + 10,200 14,400 17,000
K + 390 660 610
SO 2- 1,350 7,100 7,600
C1- 18,000 19,500 23,600
Total solids 30,970 41,957 49,850
Na/C1 0.5667 0.7385 0.7203
Ca/C1 0.0211 0.0144 0.0305
K/C1 0.02167 0.03385 0.02585
Na/Ca 26.842 51.43 23.611
Ca/Mg 0.585 16.47 2.5