Page 286 - Origin and Prediction of Abnormal Formation Pressures
P. 286
258 H.H. RIEKE, G.V. CHILINGAR AND J.O. ROBERTSON JR.
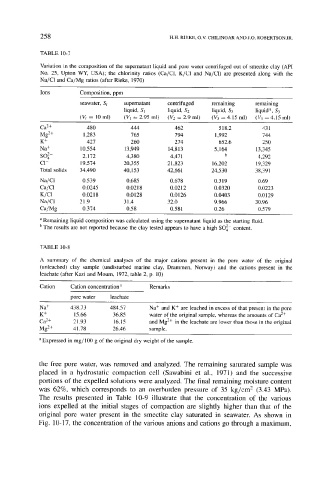
TABLE 10-7
Variation in the composition of the supernatant liquid and pore water centrifuged out of smectite clay (API
No. 25, Upton WY, USA); the chlorinity ratios (Ca/CI, K/C1 and Na/C1) are presented along with the
Na/C1 and Ca/Mg ratios (after Rieke, 1970)
Ions Composition, ppm
seawater, St supernatant centrifuged remaining remaining
liquid, S1 liquid, 82 liquid, $3 liquid a, $3
(Vt = 10 ml) (V~ = 2.95 ml) (V2 = 2.9 ml) (~ = 4.15 ml) (V3 = 4.15 ml)
Ca 2+ 480 444 462 518.2 431
Mg2+ 1,283 765 794 1,992 744
K + 427 260 274 652.6 250
Na + 10,554 13,949 14,813 5,164 13,345
SO 2- 2,172 4,380 4,471 b 4,292
C1- 19,574 20,355 21,823 16,202 19,329
Total solids 34,490 40,153 42,661 24,530 38,391
Na/C1 0.539 0.685 0.678 0.319 0.69
Ca/C1 0.0245 0.0218 0.0212 0.0320 0.0223
K/C1 0.0218 0.0128 0.0126 0.0403 0.0129
Na/C1 21.9 31.4 32.0 9.966 30.96
Ca/Mg 0.374 0.58 0.581 0.26 0.579
a Remaining liquid composition was calculated using the supernatant liquid as the starting fluid.
b The results are not reported because the clay tested appears to have a high SO42- content.
TABLE 10-8
A summary of the chemical analyses of the major cations present in the pore water of the original
(unleached) clay sample (undisturbed marine clay, Drammen, Norway) and the cations present in the
leachate (after Kazi and Mourn, 1972, table 2, p. 10)
Cation Cation concentration a Remarks
pore water leachate
Na + 438.73 484.57 Na + and K + are leached in excess of that present in the pore
K + 15.66 36.85 water of the original sample, whereas the amounts of Ca 2+
Ca e+ 21.93 16.15 and Mg 2+ in the leachate are lower than those in the original
Mg 2+ 41.78 26.46 sample.
a Expressed in mg/100 g of the original dry weight of the sample.
the free pore water, was removed and analyzed. The remaining saturated sample was
placed in a hydrostatic compaction cell (Sawabini et al., 1971) and the successive
portions of the expelled solutions were analyzed. The final remaining moisture content
was 62%, which corresponds to an overburden pressure of 35 kg/cm 2 (3.43 MPa).
The results presented in Table 10-9 illustrate that the concentration of the various
ions expelled at the initial stages of compaction are slightly higher than that of the
original pore water present in the smectite clay saturated in seawater. As shown in
Fig. 10-17, the concentration of the various anions and cations go through a maximum,