Page 103 - Photoreactive Organic Thin Films
P. 103
82 ZOUHEIR SEKKAT
0.0-
-0.1-
0.2-
0 20 40 60 8<
Time of Iratiation, t / min
•| -0.5-
•<
20 40 60 80
Time of Irradiation, t / min
A
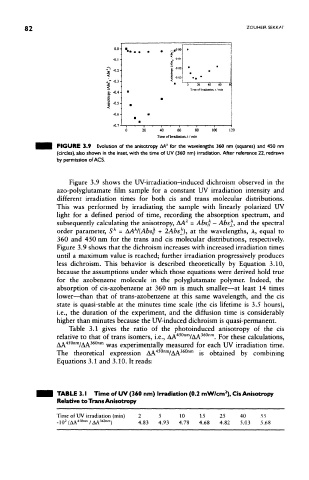
FIGURE 3.9 Evolution of the anisotropy AA for the wavelengths 360 nm (squares) and 450 nm
(circles), also shown in the inset, with the time of UV (360 nm) irradiation. After reference 22, redrawn
by permission of ACS.
Figure 3.9 shows the UV-irradiation-induced dichroism observed in the
azo-polyglutamate film sample for a constant UV irradiation intensity and
different irradiation times for both cis and trans molecular distributions.
This was performed by irradiating the sample with linearly polarized UV
light for a defined period of time, recording the absorption spectrum, and
A
subsequently calculating the anisotropy, AA = Abs// - Ab$±, and the spectral
A
order parameter, 5 = AA^/(Abs^ + 2Abs±), at the wavelengths, A, equal to
360 and 450 nm for the trans and cis molecular distributions, respectively.
Figure 3.9 shows that the dichroism increases with increased irradiation times
until a maximum value is reached; further irradiation progressively produces
less dichroism. This behavior is described theoretically by Equation 3.10,
because the assumptions under which those equations were derived hold true
for the azobenzene molecule in the polyglutamate polymer. Indeed, the
absorption of cis-azobenzene at 360 nrn is much smaller—at least 14 times
lower—than that of trans-azobenzene at this same wavelength, and the cis
state is quasi-stable at the minutes time scale (the cis lifetime is 3.5 hours),
i.e., the duration of the experiment, and the diffusion time is considerably
higher than minutes because the UV-induced dichroism is quasi-permanent.
Table 3.1 gives the ratio of the photoinduced anisotropy of the cis
450nm 360nm
relative to that of trans isomers, i.e., AA /AA . For these calculations,
450nm 360nm
AA /AA was experimentally measured for each UV irradiation time.
450nm 360nm
The theoretical expression AA /AA is obtained by combining
Equations 3.1 and 3.10. It reads:
2
TABLE 3.1 Time of UV (360 nm) Irradiation (0.2 mW/cm ), Cis Anisotropy
Relative to Trans Anisotropy
Time of UV irradiation (min) 2 5 10 15 25 40 55
2
-10 (AA 4SOnm /AA 360nm ) 4.83 4.93 4.78 4.68 4.82 5.03 5.6