Page 106 - Photoreactive Organic Thin Films
P. 106
3. PHOTO-ORIENTATION BY PHOTO1SOMERIZATION 85
(A)
• PUR-1
o PUR-2
• PUR-3
D PUR-4
Linear Fit
I 1 L
5 10
X'*10 (Einstein, s .L .cm)
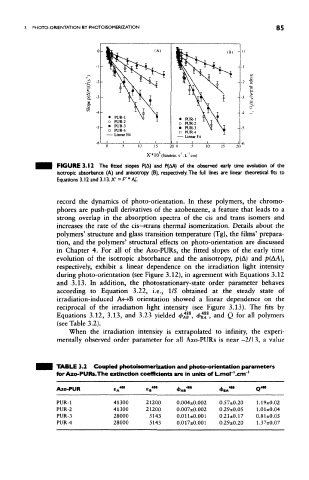
FIGURE 3.12 The fitted slopes P(A) and P(AA) of the observed early time evolution of the
isotropic absorbance (A) and anisotrop/ (B), respectively. The full lines are linear theoretical fits to
Equations 3.12 and 3.13. X' = F * A 0'.
record the dynamics of photo-orientation. In these polymers, the chromo-
phores are push-pull derivatives of the azobenzene, a feature that leads to a
strong overlap in the absorption spectra of the cis and trans isomers and
increases the rate of the cis-»trans thermal isomerization. Details about the
polymers' structure and glass transition temperature (Tg), the films' prepara-
tion, and the polymers' structural effects on photo-orientation are discussed
in Chapter 4. For all of the Azo-PURs, the fitted slopes of the early time
evolution of the isotropic absorbance and the anisotropy, p(A) and p(AA),
respectively, exhibit a linear dependence on the irradiation light intensity
during photo-orientation (see Figure 3.12), in agreement with Equations 3.12
and 3.13. In addition, the photostationary-state order parameter behaves
according to Equation 3.22, i.e., 1/S obtained at the steady state of
irradiation-induced A<-»B orientation showed a linear dependence on the
reciprocal of the irradiation light intensity (see Figure 3.13). The fits by
8
r a
Equations 3.12, 3.13, and 3.23 yielded ^f , <f>BA*-> an d Q fc> ^ polymers
(see Table 3.2).
When the irradiation intensity is extrapolated to infinity, the experi-
mentally observed order parameter for all Azo-PURs is near -2/13, a value
TABLE 3.2 Coupled photoisomerization and photo-orientation parameters
for Azo-PURs.The extinction coefficients are in units of L.moF'.cm"" 1
Azo-PUR
PUR-1 41300 21200 0.004*0.002 0.57*0.20 1.19*0.02
PUR-2 41300 21200 0.007*0.002 0.29*0.05 1.01*0.04
PUR-3 28000 5143 0.011*0.001 0.21*0.17 0.81*0.05
PUR-4 28000 5143 0.017*0.001 0.29*0.20 1.37±0.07