Page 217 - Physical chemistry understanding our chemical world
P. 217
184 PHASE EQUILIBRIA
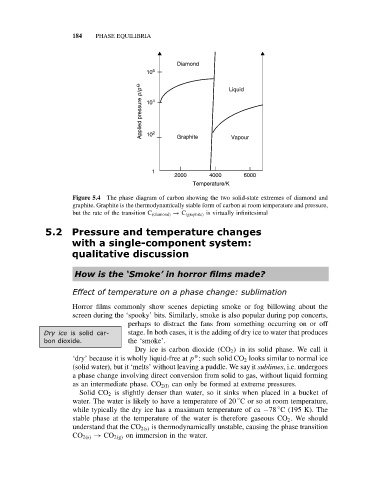
Diamond
10 6 Liquid
Applied pressure p/p O 10 4 2 Graphite Vapour
10
1
2000 4000 6000
Temperature/K
Figure 5.4 The phase diagram of carbon showing the two solid-state extremes of diamond and
graphite. Graphite is the thermodynamically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure,
but the rate of the transition C (diamond) → C (graphite) is virtually infinitesimal
5.2 Pressure and temperature changes
with a single-component system:
qualitative discussion
How is the ‘Smoke’ in horror films made?
Effect of temperature on a phase change: sublimation
Horror films commonly show scenes depicting smoke or fog billowing about the
screen during the ‘spooky’ bits. Similarly, smoke is also popular during pop concerts,
perhaps to distract the fans from something occurring on or off
Dry ice is solid car- stage. In both cases, it is the adding of dry ice to water that produces
bon dioxide. the ‘smoke’.
Dry ice is carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) in its solid phase. We call it
O
‘dry’ because it is wholly liquid-free at p : such solid CO 2 looks similar to normal ice
(solid water), but it ‘melts’ without leaving a puddle. We say it sublimes, i.e. undergoes
a phase change involving direct conversion from solid to gas, without liquid forming
as an intermediate phase. CO 2(l) can only be formed at extreme pressures.
Solid CO 2 is slightly denser than water, so it sinks when placed in a bucket of
◦
water. The water is likely to have a temperature of 20 C or so at room temperature,
◦
while typically the dry ice has a maximum temperature of ca −78 C (195 K). The
stable phase at the temperature of the water is therefore gaseous CO 2 . We should
understand that the CO 2(s) is thermodynamically unstable, causing the phase transition
CO 2(s) → CO 2(g) on immersion in the water.