Page 299 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 299
13/276 Stations and Surface Facilities
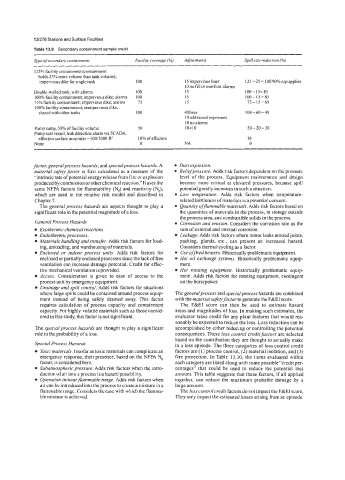
Table 13.9 Secondary containment sample credit
~
ljp of secondary containment Faciliy coverage (%) Adjustments Spill size reduction (%)
125% facility containment (containment
holds 25% more volume than tank volume);
impervious dike for single tank 100 15 impervious liner 125-25= 10090%capapplies
IO no fill or overflow alarms
Double-walled tank; with alarms LOO 15 100 - 15= 85
100% facility containment; impervious dike; alarms 100 15 100 - I5 = 85
75% facility containment; impervious dike; alarms 75 15 75-15-60
100% facility containment; semipervious dike,
shared with other tanks 100 40liner 100- 60=40
10 additional exposures
10 no alarms
Pump sump, 50% of facility volume 50 10+10 50 - 20 = 30
Pump seal vessel, leak detection alarm via SCADA,
effective surface area ratio = IOO/IOOO ftz 10% ofeffective IO
None 0 NA 0
factor, general process hazards, and special process hazards. A Dust explosion.
material safety factor is first calculated as a measure of the Reliefpressure. Adds risk factors dependent on the pressure
“intrinsic rate ofpotential energy release from fire or explosion level of the process. Equipment maintenance and design
produced by combustion or other chemical reaction.” It uses the become more critical at elevated pressures, because spill
same NFPA factors for flammability (Nf) and reactivity (NJ, potential greatly increases in such a situation.
which are used in the relative risk model and described in Low temperature. Adds risk factors when temperature-
Chapter 7. related brittleness of materials is a potential concern.
The general process hazards are aspects thought to play a Quantity offammable materials. Adds risk factors based on
significant role in the potential magnitude of a loss. the quantities of materials in the process, in storage outside
the process area, and combustible solids in the process.
General Process Hazards Corrosion and erosion. Considers the corrosion rate as the
Exothermic chemical reactions. sum ofexternal and internal corrosion.
Endothermic processes. Leakage. Adds risk factors where minor leaks around joints,
Materials handling and transfer. Adds risk factors for load- packing, glands, etc., can present an increased hazard.
ing, unloading, and warehousing of materials. Considers thermal cycling as a factor.
Enclosed or indoor process units. Adds risk factors for Use offired heaters. Historically problematic equipment.
enclosed or partially enclosed processes since the lack of free Hot oil exchange systems. Historically problematic equip-
ventilation can increase damage potential. Credit for effec- ment.
tive mechanical ventilation is provided. Hot rotating equipment. Historically problematic equip-
Access. Consideration is given to ease of access to the ment. Adds risk factors for rotating equipment, contingent
process unit by emergency equipment. on the horsepower.
Drainage and spill control. Adds risk factors for situations
where large spills could be contained around process equip- The general process and special process hazards are combined
ment instead of being safely drained away. This factor with the material safety factor to generate the F&EI score.
requires calculation of process capacity and containment The F&EI score can then be used to estimate hazard
capacity. For highly volatile materials such as those consid- areas and magnitudes of loss. In making such estimates, the
ered in this study, this factor is not significant. evaluator takes credit for any plant features that would rea-
sonably be expected to reduce the loss. Loss reduction can be
The special process hazards are thought to play a significant accomplished by either reducing or controlling the potential
role in the probability of a loss. consequences. These loss control credit factors are selected
based on the contribution they are thought to actually make
Special Process Hazards in a loss episode. The three categories of loss control credit
# Toxic materials. Insofar as toxic materials can complicate an factors are (1) process control, (2) material isolation, and (3)
emergency response, their presence, based on the NFPA Nh fire protection. In Table 13.10, the items evaluated within
factor, is considered here. each category are listed along with some possible “credit per-
Subatmospheric pressure. Adds risk factors when the intro- centages” that could be used to reduce the potential loss
duction of air into a process is a hazard possibility. amount. This table suggests that these factors, if all applied
Operation in/nearflammable range. Adds risk factors when together, can reduce the maximum probable damage by a
air can be introduced into the process to create a mixture in a large amount.
flammable range. Considers the ease with which the flamma- The loss controlcredit factors do not impact the F&EI score.
ble mixture is achieved. They only impact the estimated losses arising from an episode.