Page 171 - Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
P. 171
158 Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
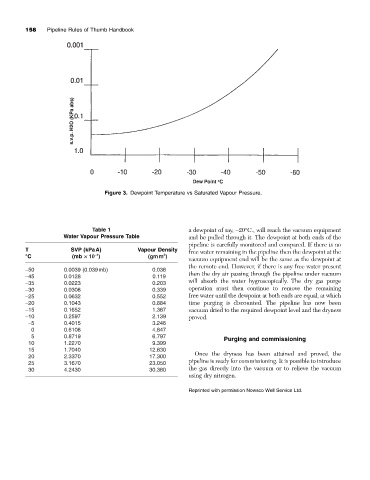
Figure 3. Dewpoint Temperature vs Saturated Vapour Pressure.
Table 1 a dewpoint of say, -20°C., will reach the vacuum equipment
Water Vapour Pressure Table and be pulled through it. The dewpoint at both ends of the
pipeline is carefully monitored and compared. If there is no
T SVP (kPaA) Vapour Density free water remaining in the pipeline then the dewpoint at the
-1
3
°C (mb ¥ 10 ) (gmm )
vacuum equipment end will be the same as the dewpoint at
the remote end. However, if there is any free water present
-50 0.0039 (0.039mb) 0.038
-45 0.0128 0.119 then the dry air passing through the pipeline under vacuum
-35 0.0223 0.203 will absorb the water hygroscopically. The dry gas purge
-30 0.0308 0.339 operation must then continue to remove the remaining
-25 0.0632 0.552 free water until the dewpoint at both ends are equal, at which
-20 0.1043 0.884 time purging is discounted. The pipeline has now been
-15 0.1652 1.387 vacuum dried to the required dewpoint level and the dryness
-10 0.2597 2.139 proved.
-5 0.4015 3.246
0 0.6108 4.847
5 0.8719 6.797
Purging and commissioning
10 1.2270 9.399
15 1.7040 12.830
20 2.3370 17.300 Once the dryness has been attained and proved, the
25 3.1670 23.050 pipeline is ready for commissioning. It is possible to introduce
30 4.2430 30.380 the gas directly into the vacuum or to relieve the vacuum
using dry nitrogen.
Reprinted with permission Nowsco Well Service Ltd.