Page 196 - Plant design and economics for chemical engineers
P. 196
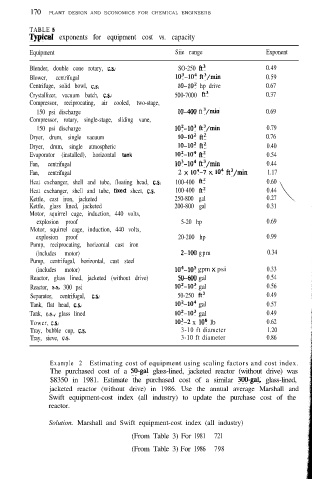
170 PLANT DESIGN AND ECONOMICS FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS
TABLE 5
ljpical exponents for equipment cost vs. capacity
Equipment Siie range Exponent
Blender, double cone rotary, C.S. SO-250 fi3 0.49
Blower, centrifugal 103-lo4 ft3/min 0.59
Centrifuge, solid bowl, C.S. lo-10’ hp drive 0.67
Crystallizer, vacuum batch, C.S. 500-7000 ft3 0.37
Compressor, reciprocating, air cooled, two-stage,
150 psi discharge 10-400 ft 3/min 0.69
Compressor, rotary, single-stage, sliding vane,
150 psi discharge lo’-lo3 ft3/min 0.79
Dryer, drum, single vacuum 10-102 ft2 0.76
Dryer, drum, single atmospheric 10-102 ft2 0.40
Evaporator (installed), horizontal tank 102-104 ft2 0.54
Fan, centrifugal lo’-lo4 ft3/min 0.44
Fan, centrifugal 2 X 104-7 X lo4 ft3/min 1.17
Heat exchanger, shell and tube, floating head, C.S. 100-400 ft2 0.60
Heat exchanger, shell and tube, fixed sheet, C.S. 100-400 ft2 0.44
Kettle, cast iron, jacketed 250-800 gal 0.27 \
Kettle, glass lined, jacketed 200-800 gal 0.31
Motor, squirrel cage, induction, 440 volts,
explosion proof 5-20 hp 0.69
Motor, squirrel cage, induction, 440 volts,
explosion proof 20-200 hp 0.99
Pump, reciprocating, horizontal cast iron
(includes motor) 2-100 gpm 0.34
Pump, centrifugal, horizontal, cast steel
(includes motor) 104-lo5 gpm X psi 0.33
Reactor, glass lined, jacketed (without drive) 50-600 gal 0.54
Reactor, s.s, 300 psi lo*-lo3 gal 0.56
Separator, centrifugal, C.S. 50-250 ft3 0.49
Tank, flat head, C.S. 102-lo4 gal 0.57
Tank, c.s., glass lined lo*-lo3 gal 0.49
Tower, C.S. 103-2 x lo6 lb 0.62
Tray, bubble cup, C.S. 3-10 ft diameter 1.20
Tray, sieve, C.S. 3-10 ft diameter 0.86
Example 2 Estimating cost of equipment using scaling factors and cost index.
The purchased cost of a 50-gal glass-lined, jacketed reactor (without drive) was
$8350 in 1981. Estimate the purchased cost of a similar 3OO-gal, glass-lined,
jacketed reactor (without drive) in 1986. Use the annual average Marshall and
Swift equipment-cost index (all industry) to update the purchase cost of the
reactor.
Solution. Marshall and Swift equipment-cost index (all industry)
(From Table 3) For 1981 721
(From Table 3) For 1986 798