Page 199 - Plant design and economics for chemical engineers
P. 199
COST ESTIMATION 173
instrumentation. This part of the capital investment is sometimes combined with
the general equipment groups. Total instrumentation cost depends on the
amount of control required and may amount to 6 to 30 percent of the purchased
cost for all equipment. Computers are commonly used with controls and have
the effect of increasing the cost associated with controls.
For the normal solid-fluid chemical processing plant, a value of 13 percent
of the purchased equipment is normally used to estimate the total instrumenta-
tion cost. This cost represents approximately 3 percent of the total capital
investment. Depending on the complexity of the instruments and the service,
additional charges for installation and accessories may amount to 50 to 70
percent of the purchased cost, with the installation charges being approximately
equal to the cost for accessories.
Piping
The cost for piping covers labor, valves, fittings, pipe, supports, and othe ‘terns
+m is
involved in the complete erection of all piping used directly in the process.
includes raw-material, intermediate-product, finished-product, steam, water, air,
sewer, and other process piping. Since process-plant piping can run as high as
80 percent of purchased-equipment cost or 20 percent of tied-capital invest-
ment, it is understandable that accuracy of the entire estimate can be seriously
affected by the improper application of estimation techniques to this one
component.
Piping estimation methods involve either some degree of piping take-off
from detailed drawings and flow sheets or using a factor technique when neither
detailed drawings nor flow sheets are available. Factoring by percent of pur-
chased-equipment cost and percent of fixed-capital investment is based strictly
on experience gained from piping costs for similar previously installed
chemical-process plants. Table 8 presents a rough estimate of the piping costs
for various types of chemical processes. Additional information for estimating
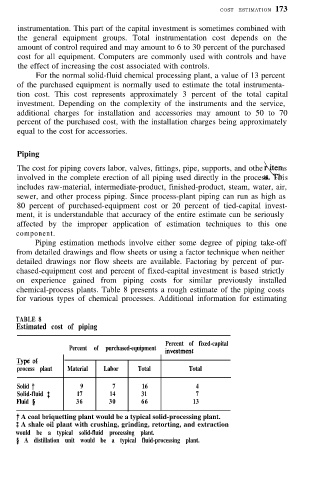
TABLE 8
Estimated cost of piping
Percent of fixed-capital
Percent of purchased-equipment investment
Type of
process plant Material Labor Total Total
Solid t 9 7 16 4
Solid-fluid $ 17 14 31 7
Fluid 0 36 30 66 13
t A coal briquetting plant would be a typical solid-processing plant.
$ A shale oil plant with crushing, grinding, retorting, and extraction
would be a typical solid-fluid processing plant.
0 A distillation unit would be a typical fluid-processing plant.