Page 44 - Power Quality in Electrical Systems
P. 44
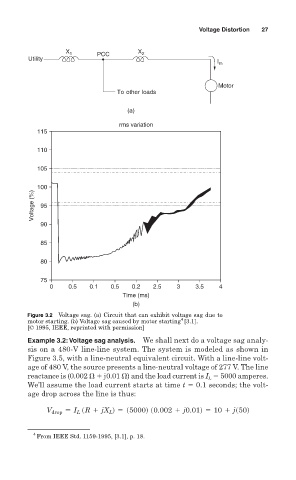
Voltage Distortion 27
X 1 PCC X 2
Utility
I m
Motor
To other loads
(a)
rms variation
115
110
105
100
Voltage (%) 95
90
85
80
75
0 0.5 0.1 0.5 0.2 2.5 3 3.5 4
Time (ms)
(b)
Figure 3.2 Voltage sag. (a) Circuit that can exhibit voltage sag due to
4
motor starting. (b) Voltage sag caused by motor starting [3.1].
[© 1995, IEEE, reprinted with permission]
Example 3.2:Voltage sag analysis. We shall next do a voltage sag analy-
sis on a 480-V line-line system. The system is modeled as shown in
Figure 3.5, with a line-neutral equivalent circuit. With a line-line volt-
age of 480 V, the source presents a line-neutral voltage of 277 V. The line
reactance is (0.002 j0.01 ) and the load current is I 5000 amperes.
L
We’ll assume the load current starts at time t 0.1 seconds; the volt-
age drop across the line is thus:
V drop 5 I sR 1 jX d 5 s5000d s0.002 1 j0.01d 5 10 1 js50d
L
L
4
From IEEE Std. 1159-1995, [3.1], p. 18.