Page 173 - Probability Demystified
P. 173
162 CHAPTER 9 The Normal Distribution
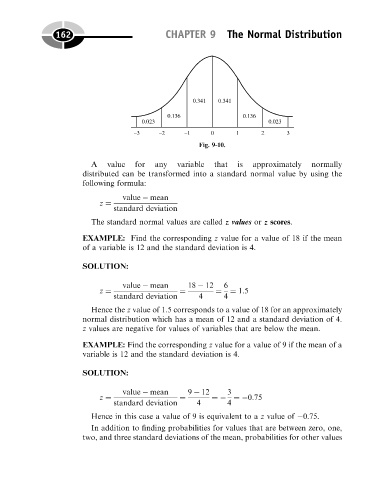
Fig. 9-10.
A value for any variable that is approximately normally
distributed can be transformed into a standard normal value by using the
following formula:
value mean
z ¼
standard deviation
The standard normal values are called z values or z scores.
EXAMPLE: Find the corresponding z value for a value of 18 if the mean
of a variable is 12 and the standard deviation is 4.
SOLUTION:
value mean 18 12 6
z ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ 1:5
standard deviation 4 4
Hence the z value of 1.5 corresponds to a value of 18 for an approximately
normal distribution which has a mean of 12 and a standard deviation of 4.
z values are negative for values of variables that are below the mean.
EXAMPLE: Find the corresponding z value for a value of 9 if the mean of a
variable is 12 and the standard deviation is 4.
SOLUTION:
value mean 9 12 3
z ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ 0:75
standard deviation 4 4
Hence in this case a value of 9 is equivalent to a z value of 0.75.
In addition to finding probabilities for values that are between zero, one,
two, and three standard deviations of the mean, probabilities for other values