Page 153 - Process Equipment and Plant Design Principles and Practices by Subhabrata Ray Gargi Das
P. 153
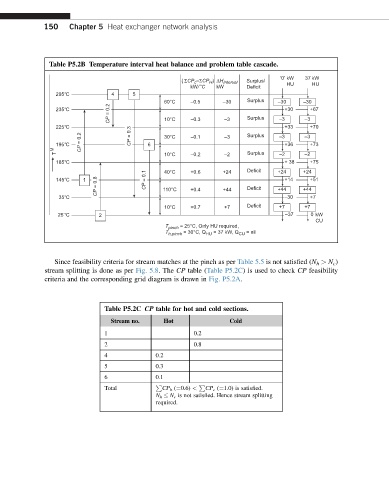
150 Chapter 5 Heat exchanger network analysis
Table P5.2B Temperature interval heat balance and problem table cascade.
( ΣCP –ΣCP ) ΔH Interval Surplus/ ‘0’ kW 37 kW
H
c
kW/ °C kW Deficit HU HU
295°C 4 5
60°C –0.5 –30 Surplus –30 –30
CP = 0.2 10°C –0.3 –3 Surplus –3 –3
235°C +30 +67
225°C +33 +70
CP = 0.2 CP = 0.3 6 30°C –0.1 –3 Surplus –3 +36 –3 +73
T M 195°C 10°C –0.2 –2 Surplus –2 –2
185°C Deficit + 38 +75
CP = 0.8 110°C +0.4 +44 Deficit +44 +44
145°C 1 CP = 0.1 40°C +0.6 +24 +24 +14 +24 +51
35°C –30 +7
10°C +0.7 +7 Deficit +7 +7
25 °C 2 –37 0 kW
CU
T pinch = 25°C, Only HU required,
T h,pinch = 30°C, Q HU = 37 kW, Q CU = nil
Since feasibility criteria for stream matches at the pinch as per Table 5.5 is not satisfied (N h > N c )
stream splitting is done as per Fig. 5.8.The CP table (Table P5.2C) is used to check CP feasibility
criteria and the corresponding grid diagram is drawn in Fig. P5.2A.
Table P5.2C CP table for hot and cold sections.
Stream no. Hot Cold
1 0.2
2 0.8
4 0.2
5 0.3
6 0.1
Total P CP h (¼0.6) < P CP c (¼1.0) is satisfied.
N h N c is not satisfied. Hence stream splitting
required.