Page 155 - Process Equipment and Plant Design Principles and Practices by Subhabrata Ray Gargi Das
P. 155
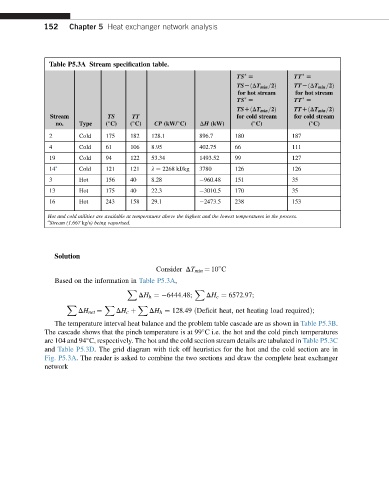
152 Chapter 5 Heat exchanger network analysis
Table P5.3A Stream specification table.
TS [ TT [
TSLðDT min =2Þ TTLðDT min =2Þ
for hot stream for hot stream
TS [ TT [
TSDðDT min =2Þ TTDðDT min =2Þ
Stream TS TT for cold stream for cold stream
no. Type ( C) ( C) CP (kW/ C) DH (kW) ( C) ( C)
2 Cold 175 182 128.1 896.7 180 187
4 Cold 61 106 8.95 402.75 66 111
19 Cold 94 122 53.34 1493.52 99 127
14 a Cold 121 121 l ¼ 2268 kJ/kg 3780 126 126
3 Hot 156 40 8.28 960.48 151 35
13 Hot 175 40 22.3 3010.5 170 35
16 Hot 243 158 29.1 2473.5 238 153
Hot and cold utilities are available at temperatures above the highest and the lowest temperatures in the process.
a
Stream (1.667 kg/s) being vaporised.
Solution
Consider DT min ¼ 10 C
Based on the information in Table P5.3A,
X X
DH h ¼ 6444.48; DH c ¼ 6572.97;
X X X
DH h ¼ 128.49 ðDeficit heat; net heating load requiredÞ;
DH net ¼ DH c þ
The temperature interval heat balance and the problem table cascade are as shown in Table P5.3B.
The cascade shows that the pinch temperature is at 99 C i.e. the hot and the cold pinch temperatures
are 104 and 94 C, respectively. The hot and the cold section stream details are tabulated in Table P5.3C
and Table P5.3D. The grid diagram with tick off heuristics for the hot and the cold section are in
Fig. P5.3A. The reader is asked to combine the two sections and draw the complete heat exchanger
network