Page 34 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 34
24 angle, Brewster angle, solid
a
tion. The angle for which f =p/2nd r is at a minimum is the The total rotation for two-way paths to 1000-km altitude
pseudo-Brewster angle, given by is shown in Fig. A44 as a function of frequency for different
elevation angles. SAL, DKB
1
sin y = ------------------
B Ref.: Berkowitz (1965), pp. 360–364; Morchin (1993), p. 328.
1 + e
r
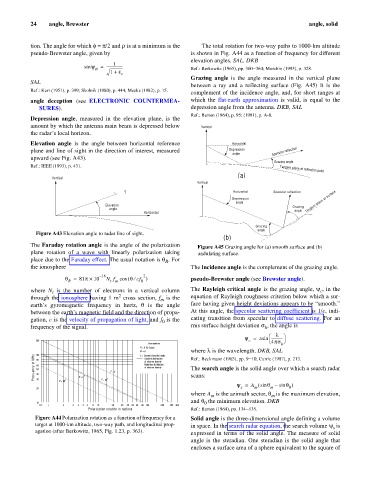
Grazing angle is the angle measured in the vertical plane
SAL
between a ray and a reflecting surface (Fig. A45) It is the
Ref.: Kerr (1951), p. 399; Skolnik (1980), p. 444; Meeks (1982), p. 15.
complement of the incidence angle, and, for short ranges at
angle deception (see ELECTRONIC COUNTERMEA- which the flat-earth approximation is valid, is equal to the
SURES). depression angle from the antenna. DKB, SAL
Ref.: Barton (1964), p. 95; (1991), p. A-8.
Depression angle, measured in the elevation plane, is the
amount by which the antenna main beam is depressed below Vertical
the radar’s local horizon.
Elevation angle is the angle between horizontal reference Horizontal
plane and line of sight in the direction of interest, measured Depression Specular reflection
angle
upward (see Fig. A43).
Grazing angle
Ref.: IEEE (1993), p. 431. Tangent plane at reflection point
(a)
Vertical
Vertical
Horizontal Specular reflection
Depression
angle Tangent plane at surface
Elevation Grazing
angle angle
Horizontal
Grazing
angle
Figure A43 Elevation angle to radar line of sight.
(b)
The Faraday rotation angle is the angle of the polarization Figure A45 Grazing angle for (a) smooth surface and (b)
plane rotation of a wave with linearly polarization taking undulating surface.
place due to the Faraday effect. The usual notation is q . For
R
the ionosphere The incidence angle is the complement of the grazing angle.
– 18 2
q = 81p 10 N f cos ( q cf ) pseudo-Brewster angle (see Brewster angle).
´
¤
R t m 0
where N is the number of electrons in a vertical column The Rayleigh critical angle is the grazing angle, y , in the
c
t
2
through the ionosphere having 1 m cross section, f is the equation of Rayleigh roughness criterion below which a sur-
m
earth’s gyromagnetic frequency in hertz, q is the angle face having given height deviations appears to be “smooth.”
between the earth’s magnetic field and the direction of propa- At this angle, the specular scattering coefficient is 1/e, indi-
gation, c is the velocity of propagation of light, and f is the cating transition from specular to diffuse scattering. For an
0
frequency of the signal. rms surface height deviation s , the angle is
h
l
y = asin æ ------------- ö
200 c è 4ps ø
Assumptions h
H = 0.62 Gauss
q E = Ground elevation angle where l is the wavelength. DKB, SAL
= 0
100
Frequency in MHz 80 60 50 40 E = 0 of electron density The search angle is the solid angle over which a search radar
Ref.: Beckmann (1963), pp. 9–10; Currie (1987), p. 213.
Daytime distribution
Nighttime distribution
of electron density
30
E = 90 o E = 0 o E = 90 o scans:
y = A ( sin q – sin q )
20 s m m 0
where A is the azimuth sector, q is the maximum elevation,
m
m
and q the minimum elevation. DKB
10 0
0.7 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 10 20 30 40 50 60 80 100 200 300 400
Polarization rotation in radians Ref.: Barton (1964), pp. 134–135.
Figure A44 Polarization rotation as a function of frequency for a Solid angle is the three-dimensional angle defining a volume
target at 1000-km altitude, two-way path, and longitudinal prop- in space. In the search radar equation, the search volume y is
s
agation (after Berkowitz, 1965, Fig. 1.23, p. 363).
expressed in terms of the solid angle. The measure of solid
angle is the steradian. One steradian is the solid angle that
encloses a surface area of a sphere equivalent to the square of