Page 37 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 37
antenna, Cassegorian antenna, conformal 27
flector is used as an aberration-correcting subreflector in con-
ical-torus scanning. SAL
Ref.: Johnson (1993), p. 17.47.
A Cassegrainian antenna is a reflector antenna comprising a
main parabolic reflector and a hyperbolic subreflector placed
between the focus and center of the main reflector (Fig. A50).
If one considers the subreflector as a hyperbolic reflector cre-
ating a mirror image of the feed at point F which is at the
r
focus of the parabola, then the antenna with a subreflector can
be considered as a conventional single-reflector parabolic
antenna, but with increased focal length. This is an important
special feature of such antennas since the increase in focal
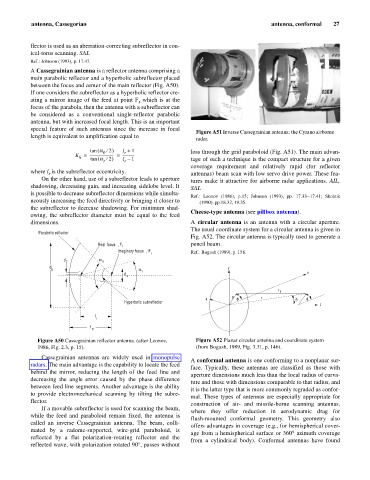
Figure A51 Inverse Cassegrainian antenna: the Cyrano airborne
length is equivalent to amplification equal to
radar.
tan ( a 2 ¤ ) l + 1 loss through the grid paraboloid (Fig. A51). The main advan-
0
r
K = -------------------------- = -------------
h tan ( a 2 ¤ ) l – 1 tage of such a technique is the compact structure for a given
r r
coverage requirement and relatively rapid (for reflector
where l is the subreflector eccentricity. antennas) beam scan with low servo drive power. These fea-
r
On the other hand, use of a subreflector leads to aperture tures make it attractive for airborne radar applications. AIL,
shadowing, decreasing gain, and increasing sidelobe level. It SAL
is possible to decrease subreflector dimensions while simulta-
Ref.: Leonov (1986), p.15; Johnson (1993), pp. 17.33–17.41; Skolnik
neously increasing the feed directivity or bringing it closer to (1990), pp.18.32, 19.35.
the subreflector to decrease shadowing. For minimum shad-
Cheese-type antenna (see pillbox antenna).
owing, the subreflector diameter must be equal to the feed
dimensions. A circular antenna is an antenna with a circular aperture.
The usual coordinate system for a circular antenna is given in
Parabolic reflector
Fig. A52. The circular antenna is typically used to generate a
Real focus , F r pencil beam.
Imaginary focus , F Ref.: Bogush (1989), p. 158.
i
d f a 0
d p a y
d r x
s
r 0
r
a f r q f
Hyperbolic subreflector
z
f
r
f p
Figure A50 Cassegrainian reflector antenna. (after Leonov, Figure A52 Planar circular antenna and coordinate system
1986, Fig. 2.3, p. 15). (from Bogush, 1989, Fig. 3.31, p. 146).
Cassegrainian antennas are widely used in monopulse
A conformal antenna is one conforming to a nonplanar sur-
radars. The main advantage is the capability to locate the feed
face. Typically, these antennas are classified as those with
behind the mirror, reducing the length of the feed line and
aperture dimensions much less than the local radius of curva-
decreasing the angle error caused by the phase difference
ture and those with dimensions comparable to that radius, and
between feed line segments. Another advantage is the ability
it is the latter type that is more commonly regraded as confor-
to provide electromechanical scanning by tilting the subre-
mal. These types of antennas are especially appropriate for
flector.
construction of air- and missile-borne scanning antennas,
If a movable subreflector is used for scanning the beam,
where they offer reduction in aerodynamic drag for
while the feed and paraboloid remain fixed, the antenna is
flush-mounted conformal geometry. This geometry also
called an inverse Cassegrainian antenna. The beam, colli-
offers advantages in coverage (e.g., for hemispherical cover-
mated by a radome-supported, wire-grid paraboloid, is
age from a hemispherical surface or 360° azimuth coverage
reflected by a flat polarization-rotating reflector and the
from a cylindrical body). Conformal antennas have found
reflected wave, with polarization rotated 90°, passes without