Page 33 - Rashid, Power Electronics Handbook
P. 33
2 The Power Diode 17
FIGURE 2.3 Diode reverse recovery process with various softness factors. (a) Soft recovery; and (b) abrupt recovery.
Diode Capacitance C is the net diode capacitance includ-
D
ing the junction (C ) plus package capacitance (C ).
P
J
In high-frequency pulse switching a parameter known
as transient thermal resistance is of vital importance
because it indicates the instantaneous junction tempera-
ture as a function of time under constant input power.
2.3 Common Diode Types
Depending on their applications, diodes can be segregated into
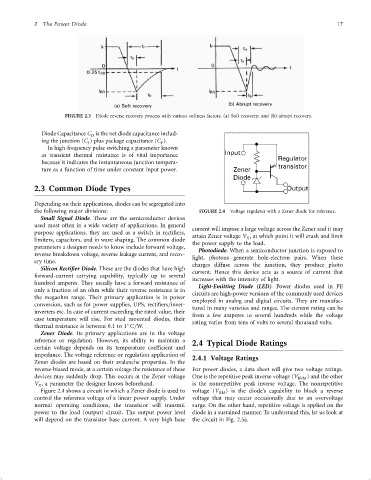
the following major divisions: FIGURE 2.4 Voltage regulator with a Zener diode for reference.
Small Signal Diode. These are the semiconductor devices
used most often in a wide variety of applications. In general
current will impose a large voltage across the Zener and it may
purpose applications, they are used as a switch in recti®ers,
attain Zener voltage V , at which point it will crush and limit
X
limiters, capacitors, and in wave shaping. The common diode
the power supply to the load.
parameters a designer needs to know include forward voltage, Photodiode. When a semiconductor junction is exposed to
reverse breakdown voltage, reverse leakage current, and recov- light, photons generate hole-electron pairs. When these
ery time. charges diffuse across the junction, they produce photo
Silicon Recti®er Diode. These are the diodes that have high
current. Hence this device acts as a source of current that
forward-current carrying capability, typically up to several
increases with the intensity of light.
hundred amperes. They usually have a forward resistance of
Light-Emitting Diode (LED). Power diodes used in PE
only a fraction of an ohm while their reverse resistance is in
circuits are high-power versions of the commonly used devices
the megaohm range. Their primary application is in power
employed in analog and digital circuits. They are manufac-
conversion, such as for power supplies, UPS, recti®ers=inver-
tured in many varieties and ranges. The current rating can be
inverters etc. In case of current exceeding the rated value, their
from a few amperes to several hundreds while the voltage
case temperature will rise. For stud mounted diodes, their rating varies from tens of volts to several thousand volts.
thermal resistance is between 0.1 to 1 C=W.
Zener Diode. Its primary applications are in the voltage
reference or regulation. However, its ability to maintain a 2.4 Typical Diode Ratings
certain voltage depends on its temperature coef®cient and
impedance. The voltage reference or regulation application of 2.4.1 Voltage Ratings
Zener diodes are based on their avalanche properties. In the
reverse-biased mode, at a certain voltage the resistance of these For power diodes, a data sheet will give two voltage ratings.
devices may suddenly drop. This occurs at the Zener voltage One is the repetitive peak inverse voltage (V RRM ) and the other
V , a parameter the designer knows beforehand. is the nonrepetitive peak inverse voltage. The nonrepetitive
X
Figure 2.4 shows a circuit in which a Zener diode is used to voltage (V RM ) is the diode's capability to block a reverse
control the reference voltage of a linear power supply. Under voltage that may occur occasionally due to an overvoltage
normal operating conditions, the transistor will transmit surge. On the other hand, repetitive voltage is applied on the
power to the load (output) circuit. The output power level diode in a sustained manner. To understand this, let us look at
will depend on the transistor base current. A very high base the circuit in Fig. 2.5a.