Page 148 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 148
Design of Residential Photovoltaic Systems 135
Altitude of the sun above the horizontal over the whole year
60
Dec-21
Jun-21
Position of the SUN over the horizon in degrees 40 May-21
50
Feb-21
Mar-21
Apr-21
Jun-21
30
20
10
0
4:00 8:00 12:00 16:00 20:00
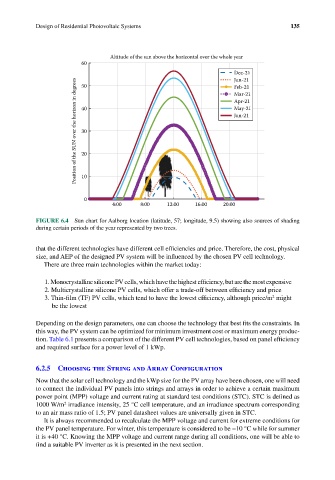
FIGURE 6.4 Sun chart for Aalborg location (latitude, 57; longitude, 9.5) showing also sources of shading
during certain periods of the year represented by two trees.
that the different technologies have different cell efficiencies and price. Therefore, the cost, physical
size, and AEP of the designed PV system will be influenced by the chosen PV cell technology.
There are three main technologies within the market today:
1. Monocrystalline silicone PV cells, which have the highest efficiency, but are the most expensive
2. Multicrystalline silicone PV cells, which offer a trade-off between efficiency and price
3. Thin-film (TF) PV cells, which tend to have the lowest efficiency, although price/m might
2
be the lowest
Depending on the design parameters, one can choose the technology that best fits the constraints. In
this way, the PV system can be optimized for minimum investment cost or maximum energy produc-
tion. Table 6.1 presents a comparison of the different PV cell technologies, based on panel efficiency
and required surface for a power level of 1 kWp.
6.2.5 Choosing the String and Array Configuration
Now that the solar cell technology and the kWp size for the PV array have been chosen, one will need
to connect the individual PV panels into strings and arrays in order to achieve a certain maximum
power point (MPP) voltage and current rating at standard test conditions (STC). STC is defined as
1000 W/m irradiance intensity, 25 °C cell temperature, and an irradiance spectrum corresponding
2
to an air mass ratio of 1.5; PV panel datasheet values are universally given in STC.
It is always recommended to recalculate the MPP voltage and current for extreme conditions for
the PV panel temperature. For winter, this temperature is considered to be −10 °C while for summer
it is +40 °C. Knowing the MPP voltage and current range during all conditions, one will be able to
find a suitable PV inverter as it is presented in the next section.