Page 97 -
P. 97
4.5 Analysis of variance 83
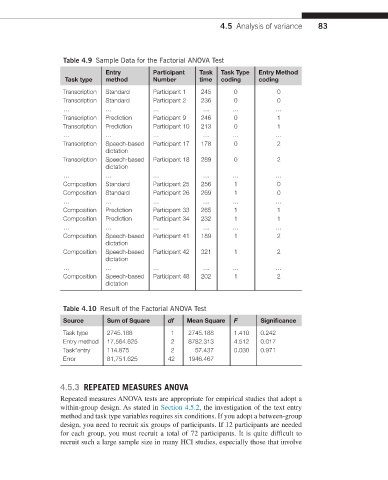
Table 4.9 Sample Data for the Factorial ANOVA Test
Entry Participant Task Task Type Entry Method
Task type method Number time coding coding
Transcription Standard Participant 1 245 0 0
Transcription Standard Participant 2 236 0 0
… … … … … …
Transcription Prediction Participant 9 246 0 1
Transcription Prediction Participant 10 213 0 1
… … … … … …
Transcription Speech-based Participant 17 178 0 2
dictation
Transcription Speech-based Participant 18 289 0 2
dictation
… … … … … …
Composition Standard Participant 25 256 1 0
Composition Standard Participant 26 269 1 0
… … … … … …
Composition Prediction Participant 33 265 1 1
Composition Prediction Participant 34 232 1 1
… … … … … …
Composition Speech-based Participant 41 189 1 2
dictation
Composition Speech-based Participant 42 321 1 2
dictation
… … … … … …
Composition Speech-based Participant 48 202 1 2
dictation
Table 4.10 Result of the Factorial ANOVA Test
Source Sum of Square df Mean Square F Significance
Task type 2745.188 1 2745.188 1.410 0.242
Entry method 17,564.625 2 8782.313 4.512 0.017
Task*entry 114.875 2 57.437 0.030 0.971
Error 81,751.625 42 1946.467
4.5.3 REPEATED MEASURES ANOVA
Repeated measures ANOVA tests are appropriate for empirical studies that adopt a
within-group design. As stated in Section 4.5.2, the investigation of the text entry
method and task type variables requires six conditions. If you adopt a between-group
design, you need to recruit six groups of participants. If 12 participants are needed
for each group, you must recruit a total of 72 participants. It is quite difficult to
recruit such a large sample size in many HCI studies, especially those that involve