Page 93 - Science at the nanoscale
P. 93
RPS: PSP0007 - Science-at-Nanoscale
7:6
June 12, 2009
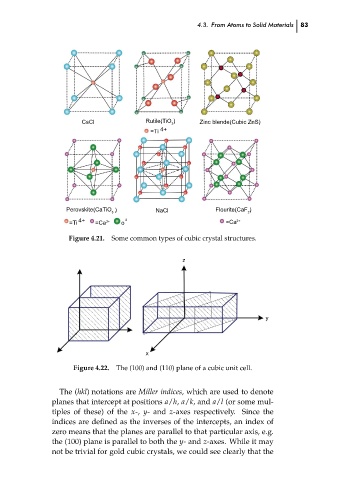
Zinc blende(Cubic ZnS)
CsCl
2
4+
=Ti
Flourite(CaF )
NaCl
Perovskite(CaTiO )
2
3
4+
2−
=Ca
2+
o
=Ca
=Ti
2+
Figure 4.21.
Some common types of cubic crystal structures.
y
x Rutile(TiO ) z 4.3. From Atoms to Solid Materials 83 ch04
Figure 4.22. The (100) and (110) plane of a cubic unit cell.
The (hkl) notations are Miller indices, which are used to denote
planes that intercept at positions a/h, a/k, and a/l (or some mul-
tiples of these) of the x-, y- and z-axes respectively. Since the
indices are defined as the inverses of the intercepts, an index of
zero means that the planes are parallel to that particular axis, e.g.
the (100) plane is parallel to both the y- and z-axes. While it may
not be trivial for gold cubic crystals, we could see clearly that the