Page 261 - Semiconductor For Micro- and Nanotechnology An Introduction For Engineers
P. 261
Interacting Subsystems
7.3.4 Piezoelectric Transducers
Let us now consider an application of an integrated viscosity sensor
based on a piezoelectric thin film [7.5]. The idea is to generate shear sur-
face waves in a transducer that is in contact with a liquid. The shear
waves are attenuated by the liquid as a function of the liquid’s viscosity.
The best sensor avoids generating out-of-plane displacements, for these
are radiated as acoustic waves and cause huge energy losses. The piezo-
electric thin film, such as PZT or ZnO, deposited on the chip’s surface, is
contacted with evaporated gold electrodes that are formed in an interdigi-
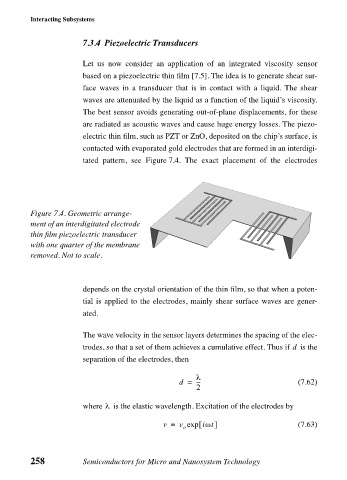
tated pattern, see Figure 7.4. The exact placement of the electrodes
Figure 7.4. Geometric arrange-
ment of an interdigitated electrode
thin film piezoelectric transducer
with one quarter of the membrane
removed. Not to scale.
depends on the crystal orientation of the thin film, so that when a poten-
tial is applied to the electrodes, mainly shear surface waves are gener-
ated.
The wave velocity in the sensor layers determines the spacing of the elec-
trodes, so that a set of them achieves a cumulative effect. Thus if is the
d
separation of the electrodes, then
λ
d = --- (7.62)
2
λ
where is the elastic wavelength. Excitation of the electrodes by
v = v exp [ iωt] (7.63)
o
258 Semiconductors for Micro and Nanosystem Technology