Page 305 - Semiconductor For Micro- and Nanotechnology An Introduction For Engineers
P. 305
Interacting Subsystems
Unbiased
2
Junction For an unbiased junction, we expect charge neutrality at distances far . 0
from the junction where the potential is constant, i.e., where ∇ ψ =
This can be expressed as
+ -
p + N = n + N (7.151)
d a
i.e., the sum of the number of holes and ionized donors (the positive
charges in the crystal) must equal the sum of the number of electrons and
ionized acceptors. The ionization is governed by fermion statistics, which
leads us to write (7.151) as
– E F N d
N Exp ---------( ) + ----------------------------------------------
c
k T E – E
B d F
1 + Exp -------------------–( )
k T
B
(7.152a)
E – E g N a
F
= N Exp ------------------( ) + ------------------------------------------
v
k T E – E F
B
a
1 + Exp ------------------( k T )
B
3 3
--- ---
h B
e B
2πm k T 2 2πm k T 2
where N = 2 ----------------------- and N = 2 ----------------------- (7.153a)
c
v
2
2
h h
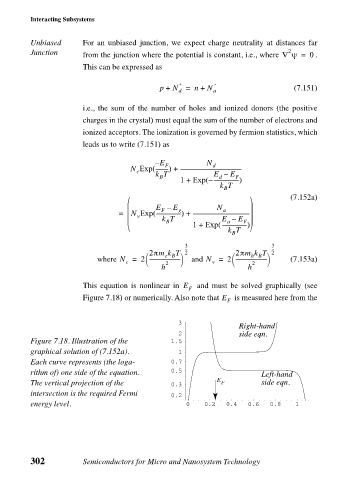
This equation is nonlinear in E F and must be solved graphically (see
Figure 7.18) or numerically. Also note that E F is measured here from the
3
Right-hand
2 side eqn.
Figure 7.18. Illustration of the 1.5
graphical solution of (7.152a). 1
Each curve represents (the loga- 0.7
rithm of) one side of the equation. 0.5 Left-hand
E
The vertical projection of the 0.3 F side eqn.
intersection is the required Fermi 0.2
energy level. 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
302 Semiconductors for Micro and Nanosystem Technology