Page 321 - Semiconductor For Micro- and Nanotechnology An Introduction For Engineers
P. 321
Interacting Subsystems
SCL
ψ SCL ψ SCL E SCL E
E E n n
p p
ρ ρ
10µm 2.5µm 10µm 2.5µm
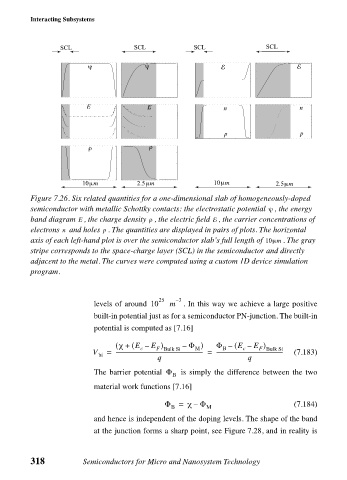
Figure 7.26. Six related quantities for a one-dimensional slab of homogeneously-doped
semiconductor with metallic Schottky contacts: the electrostatic potential , the energy
ψ
band diagram , the charge density , the electric field , the carrier concentrations of
ρ
E
E
electrons and holes . The quantities are displayed in pairs of plots. The horizontal
p
n
axis of each left-hand plot is over the semiconductor slab’s full length of 10µm . The gray
stripe corresponds to the space-charge layer (SCL) in the semiconductor and directly
adjacent to the metal. The curves were computed using a custom 1D device simulation
program.
25 – 3
levels of around 10 m . In this way we achieve a large positive
built-in potential just as for a semiconductor PN-junction. The built-in
potential is computed as [7.16]
( χ + ( E – E ) – Φ ) Φ – ( E – E )
c
M
c
B
F Bulk Si
F Bulk Si
V = ----------------------------------------------------------------- = -------------------------------------------------- (7.183)
bi
q q
The barrier potential Φ is simply the difference between the two
B
material work functions [7.16]
Φ B = χΦ M (7.184)
–
and hence is independent of the doping levels. The shape of the band
at the junction forms a sharp point, see Figure 7.28, and in reality is
318 Semiconductors for Micro and Nanosystem Technology