Page 40 - Semiconductor For Micro- and Nanotechnology An Introduction For Engineers
P. 40
Observed Lattice Property Data
o
stable below 573 C
, with trigonal crystal symmetry. The unit cell of the
quartz crystal is formed by two axes, called X and X , at 60° to each
1 2
other, see Figure 2.5. Quartz is non-centro-symmetric and hence piezo-
electric. It also has a handedness as shown in Figure 2.6.
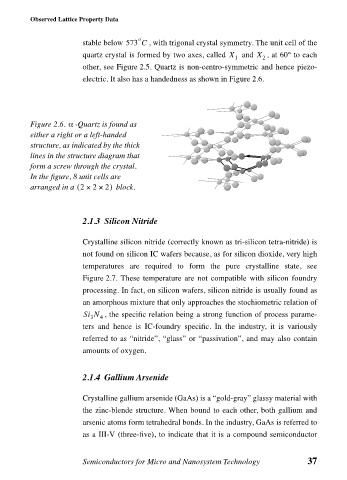
α
Figure 2.6. -Quartz is found as
either a right or a left-handed
structure, as indicated by the thick
lines in the structure diagram that
form a screw through the crystal.
In the figure, 8 unit cells are
(
arranged in a 2 × × 2) block.
2
2.1.3 Silicon Nitride
Crystalline silicon nitride (correctly known as tri-silicon tetra-nitride) is
not found on silicon IC wafers because, as for silicon dioxide, very high
temperatures are required to form the pure crystalline state, see
Figure 2.7. These temperature are not compatible with silicon foundry
processing. In fact, on silicon wafers, silicon nitride is usually found as
an amorphous mixture that only approaches the stochiometric relation of
Si N , the specific relation being a strong function of process parame-
3 4
ters and hence is IC-foundry specific. In the industry, it is variously
referred to as “nitride”, “glass” or “passivation”, and may also contain
amounts of oxygen.
2.1.4 Gallium Arsenide
Crystalline gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a “gold-gray” glassy material with
the zinc-blende structure. When bound to each other, both gallium and
arsenic atoms form tetrahedral bonds. In the industry, GaAs is referred to
as a III-V (three-five), to indicate that it is a compound semiconductor
Semiconductors for Micro and Nanosystem Technology 37