Page 36 - Semiconductor For Micro- and Nanotechnology An Introduction For Engineers
P. 36
Observed Lattice Property Data
2.1.1 Silicon
A semiconductor quality Silicon ingot is a gray, glassy, face-centered
crystal. The element is found in column IV of the periodic table. It has
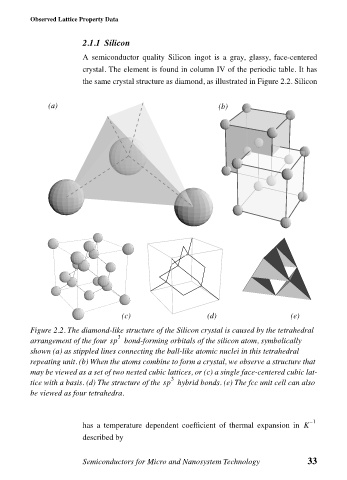
the same crystal structure as diamond, as illustrated in Figure 2.2. Silicon
(a) (b)
(c) (d) (e)
Figure 2.2. The diamond-like structure of the Silicon crystal is caused by the tetrahedral
3
arrangement of the four sp bond-forming orbitals of the silicon atom, symbolically
shown (a) as stippled lines connecting the ball-like atomic nuclei in this tetrahedral
repeating unit. (b) When the atoms combine to form a crystal, we observe a structure that
may be viewed as a set of two nested cubic lattices, or (c) a single face-centered cubic lat-
3
tice with a basis. (d) The structure of the sp hybrid bonds. (e) The fcc unit cell can also
be viewed as four tetrahedra.
– 1
has a temperature dependent coefficient of thermal expansion in K
described by
Semiconductors for Micro and Nanosystem Technology 33