Page 39 - Semiconductor For Micro- and Nanotechnology An Introduction For Engineers
P. 39
The Crystal Lattice System
IC process quality LPCVD poly-crystalline silicon (Poly-Si) has proper-
ties that depend strongly on the foundry of origin. It is assumed to be iso-
tropic in the plane of the wafer, and is mainly used as a thin film thermal
and electrical conductor for electronic applications, and as a structural
and electrode material for MEMS devices.
2.1.2 Silicon Dioxide
Crystalline silicon dioxide is better known as fused quartz. It is unusual
to obtain quartz from a silicon-based process, say CMOS, because the
production of crystalline quartz usually requires very high temperatures
that would otherwise destroy the carefully produced doping profiles in
the silicon. Semiconductor-related silicon dioxide is therefore typically
amorphous.
Since quartz has a non-cubic crystal structure, and therefore displays use-
ful properties that are not found in high-symmetry cubic systems such as
silicon, yet are of importance to microsystems, we also include it in our
discussion. We consider α -quartz, one of the variants of quartz that is
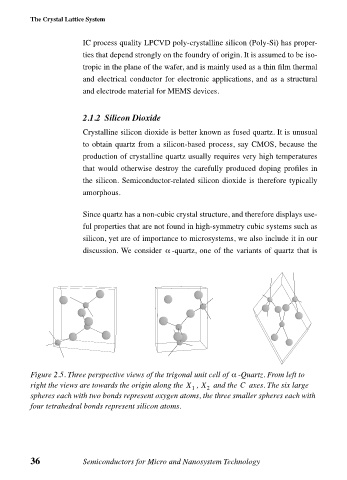
α
Figure 2.5. Three perspective views of the trigonal unit cell of -Quartz. From left to
C
right the views are towards the origin along the X , X and the axes. The six large
1 2
spheres each with two bonds represent oxygen atoms, the three smaller spheres each with
four tetrahedral bonds represent silicon atoms.
36 Semiconductors for Micro and Nanosystem Technology